(The 96901 Unit of the Chinese People's Liberation Army, Beijing 100094,China)
physical chemistry; explosion heat; isothermal calorimeter; data before malfunction; steady identification
DOI: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.202001022
备注
针对恒温法爆热经典测量方法存在测量时间长、出现系统故障易导致测量失败等问题,提出一种基于故障前数据辨识爆热的解决方案。首先建立了基于炸药瞬态反应假设的量热计传热学方程,解算得到内桶水温的变化规律; 然后基于系统辨识的思想,给出了先辨识中间参数kNW/(cNmN)、u1、λ1、λ2,然后辨识目标参数TE(τM)、kNZ/cNmN、kNZ/cZmZ,再辨识修正温升与爆热的系统辨识方法,误差分析表明爆热的辨识值可稳健地收敛于经典值,氧化、燃烧等非瞬态反应对辨识精度的影响可忽略; 最后,针对8个典型炸药样本爆热测量数据进行模拟分析并提出收敛时刻的试验判据。模拟结果表明,爆热的辨识值可在不超过3%的相对误差、1/2主末期时间的条件下快速、可靠地收敛于经典值,试验判据能可靠地判断爆热辨识值的收敛时刻,有效降低了系统故障导致测量失败的风险。
In view of the problems of the classical measurement method of constant temperature explosion heat, such as long measurement time, system failure and so on, a solution of identifying explosion heat based on prefault data was proposed. Initially, the heat transfer equation of calorimeter based on the hypothesis of explosive transient response was established, and the change rule of water temperature in inner barrel was obtained after solving. Based on the thought of system identification, the system identification method was obtained, which firstly identifies the indirect parameters of kNW/(cNmN), u1, λ1, λ2, secondly identifies the target parameters of TE(τM), kNZ/cNmN, kNZ/cZmZ, thirdly identifies the correctional raising temperature and explosion heat. The error analysis shows that the identification value of explosion heat can converge to the classical value steadily, and the influence of non transient reaction such as oxidation and combustion on the identification accuracy can be ignored. Ultimately, 8 kinds of typical explosive samples were simulated and analyzed, and the criterion of convergence time was proposed. The simulation results show that the identification value of detonation heat can converge to the classical value quickly and reliably under the condition of less than 3% relative error and 1/2 of the main and final stage. The test criterion can judge the convergence time of the identification value of detonation heat reliably and effectively reduce the risk of measurement failure caused by system fault.
引言
目前,炸药爆热的精确测量方法主要有恒温法与绝热法[1-8],两种方法均需测量内桶水的终点温度。其中,恒温法外桶温度无需跟踪内桶温度,但修正温升需要计算补偿; 而绝热法外桶温度需要跟踪内桶温度,但修正温升无需计算补偿。
由于恒温法避免了绝热法外桶跟踪内桶温度在炸药点火后短时间精度不足的问题,因此是测量质量较大炸药爆热的主要手段,但由于炸药总放热量大,经典恒温法测量时间比较长。GJB772A-97方法701.1“爆热-恒温法和绝热法”中规定了恒温法初期与末期时间均为11min,而范桂荣[9]提出将初期与末期时间延长为21min、主期时间为80min时可有效减少偶然误差。如炸药起爆后出现系统故障(系统断电、异常加温、软件崩溃等)而导致无法获取内桶水的准确终点温度,则该次试验宣告失败,将造成炸药样品报废。
为降低系统故障导致测量失败的风险,本研究提出了基于故障前测量数据利用系统辨识方法计算爆热的解决方案。根据这一思想,首先基于量热计传热方程推导分析内桶水温度温升曲线,然后基于系统辨识的思想给出炸药爆热的辨识算法,并分析系统辨识算法的收敛特性与辨识误差,最后结合西安火炸药一级计量站的试验数据验证本方法的准确性与可行性,以期为恒温法测爆热提供有益补充。
1 爆热测量原理与算法
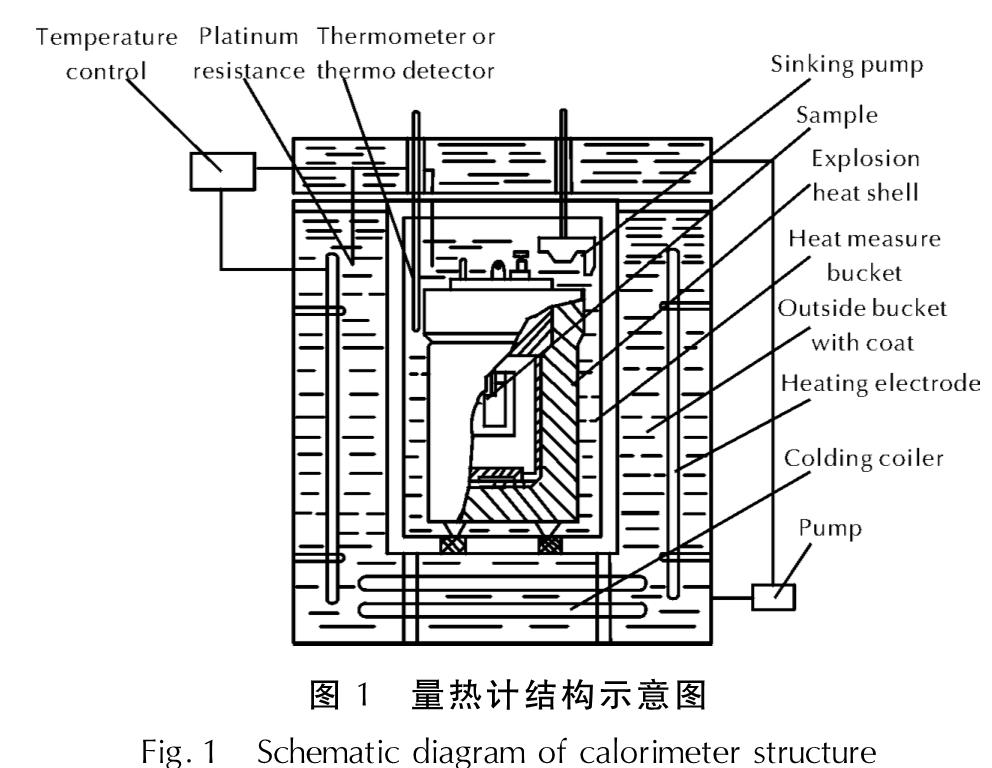
量热计结构见图1,包括内桶系统与外桶系统。内桶系统由爆热弹、量热桶组成,主要用于起爆炸药并容纳爆炸产物、吸收爆炸产物与外桶的传热量并测量炸药的爆热; 外桶系统由外桶水、套夹、温控系统等组成,用于产生一个理想的外部温度环境。内外桶通过绝热良好的支撑连接。
恒温法测爆热经典计算公式如下[1,7,9]:
Δθ=(vn-v0)/(θn-θ0)[(TI(τ0)+TI(τn))/2+
∑n-1i=1TI(τi)+n(θnv0-vnθ0)/(vn-v0)]Δτ(1)
ΔtJ=TI(τn)-TI(τ0)-Δθ(2)
Q1=(CΔt-M2Q2-q)/(M1)(3)
式中:ΔtJ、Δt为经典方法、所有方法的内桶水修正温升,℃; Δτ为采样时间间隔, min; TI(τ0)、TI(τn)分别为内桶主期初温和主期末温的数值,℃; θ0、θn分别为拟合得到初期与末期的起点温度,℃; v0、vn分别为拟合得到初期与末期的温升速率,℃/min; Δθ为温度修正值,℃; n为内桶的主期温度读数个数; Q1为被测炸药爆热,J/g; C为量热计系统热容,J/℃; M2为传爆药质量,g; Q2为传爆药爆热,J/g; q为雷管爆热,J; M1为被测炸药质量,g。
1.1 量热计的传热学分析爆热弹金属壳与内桶水容器外壳均为金属结构,导热良好,因此,可忽略金属壳体内外表面温差,即认为整个内桶系统温度是一致的,则爆炸产物向内桶系统的传热可视为对流传热[10],对应热流量ΦN1(τ)为:
ΦN1(τ)=(dQN1(τ))/(dτ)=hNAN(TE(τ)-TL(τ))=
kNZ(TE(τ)-TL(τ))(4)
式中:QN1(τ)为炸药点火时刻τM至τ爆炸产物向内桶系统的导热热量; hN为爆炸产物的对流表面传热系数; AN为爆热弹金属壳的内表面积,kNZ=hNAN; TE(τ)、TI(τ)分别为爆炸产物、内桶水在时刻τ的测量温度。
外桶系统向内桶系统的传热包括绝热支撑的热传导与热辐射等两种形式,在内外桶温差较小时可认为热辐射的热流量与内外桶温差成正比,因此,外桶系统向内桶系统传热的热流量ΦI2(τ)为:
ΦI2(τ)=(dQI2(τ))/(dτ)=-kNW(TI(τ)-TW)(5)
式中:QI2(τ)为时刻τC至τ外桶系统向内桶系统的导热热量(为方便计算,初期阶段传热学方程中,τC取初期起始时刻τS; 主末期阶段传热学方程中,τC取炸药点火时刻τM); TW为外桶水升温结束且稳定后的温度; kNW为综合热传导与热辐射的导热系数。
由于搅拌内桶水会产热,因此,调节内外桶热平衡时,内桶系统温度须高于外桶系统温度(该温差记为TC),以便将搅拌热传导至外桶,即搅拌热QC(τ)须满足:
(d)/(dτ)(QC(τ)+QInitialI2(τ))=
0(dQC(τ))/(dτ)=kNWTC(6)
初期阶段是指炸药点火前外桶水升温结束且已稳定的时间阶段。根据能量守恒定律,内桶系统的温升由外桶系统向内桶系统传热以及搅拌热的总热量确定,则有:
QI2(τ)+QC(τ)=cNmN(TI(τ)-Tl(τS))(7)
式中:cN、mN分别为内桶系统的比热容与质量。
综合式(5)、式(6)、式(7)可得初期阶段的传热学方程如下:
(d)/(dτ)(QI2(τ)+QC(τ))=-(kNW)/(cNmN)[QI2(τ)+
QC(τ)-cNmN(TW-TI(τS)+TC)](8)
主期与末期阶段分别指炸药点火至爆炸产物放热基本结束和之后的时间段。根据能量守恒定律,内桶系统的温升由爆炸产物与外桶系统向内桶系统传热以及搅拌热的总热量确定,则有:
QN1(τ)+QI2(τ)+QC(τ)=
cNmN(TI(τ)-TI(τM))(9)
式中:τM表示主期阶段的起始时刻,即炸药点火时刻,因此,τ≥τM。
这里假设炸药点火后的产热是瞬态的,点火后爆炸产物一直处于放热过程,则有:
QN1(τ)=cZmZ(TE(τM)-TE(τ))(10)
式中:cZ、mZ、TE(τM)表示爆炸产物的比热容、质量与初始温度,且τ≥τM。
综合式(4)、(5)、(6)、(9)、(10),可得主期与末期阶段传热学方程为:
{(dQN1(τ))/(dτ)=-kNZ(1/(cZmZ)+1/(cNmN))QN1(τ)-(kNZ)/(cNmN)(QI2(τ)+QC(τ))+kNZ(TE(τM)-TI(τM))
(d)/(dτ)(QI2(τ)+QC(τ))=-(kNW)/(cNmN)QN1(τ)-(kNW)/(cNmN)(QI2(τ)+QC(τ))+kNW(TW-TI(τM)+TC)(11)
1.2 量热计传热学方程解算结果根据初期阶段的传热学方程,初期阶段内桶水温度曲线计算结果为:
T⌒l(τ)=TW+TC+(TI(τS)-TW-TC)
exp(-(kNW)/(cNmN)(τ-τS))(12)
式中:T⌒I(τ)为内桶水温度在采样时间τ的理论值,且采样时间满足τS≤τ<τM。
可见,初期阶段内桶水温度变化服从指数分布规律,并且收敛于TW+TC。
根据主期与末期阶段的传热学方程,主期与末期阶段内桶水温度曲线计算结果为:
T⌒I(τ)=TW+TC+u1exp(λ1(τ-τM))+
(TI(τM)-TC-TW-u1)exp(λ2(τ-τM))(13)
式中:T⌒I(τ)为内桶水温度在采样时间τ的理论值,且采样时间满足τ≥τM; 中间参数u1、λ1、λ2的表达式如下:
u1=((TE(τM)-TI(τM))(kNZ)/(cNmN))/((Δ)1/2)-
((TW+TC-TI(τM))((kNZ-kNW)/(cNmN)+(kNZ)/(cZmZ)+(Δ)1/2))/(2(Δ)1/2)(14)
λ1=(-((kNZ)/(cZmZ)+(kNZ+kNW)/(cNmN))+(Δ)1/2)/2(15)
λ2=(-((kNZ)/(cZmZ)+(kNZ+kNW)/(cNmN))-(Δ)1/2)/2(16)
Δ=((kNZ)/(cZmZ)+(kNZ+kNW)/(cNmN))2-4(kNZ)/(cZmZ)(kNW)/(cNmN)(17)
根据式(13)~式(17),易证,λ1、λ2均为负数,且λ1>λ2; 当测量时间足够长,内桶水温度将收敛于TW+TC。
2 爆热计算的稳健辨识方法
3 试验仿真分析
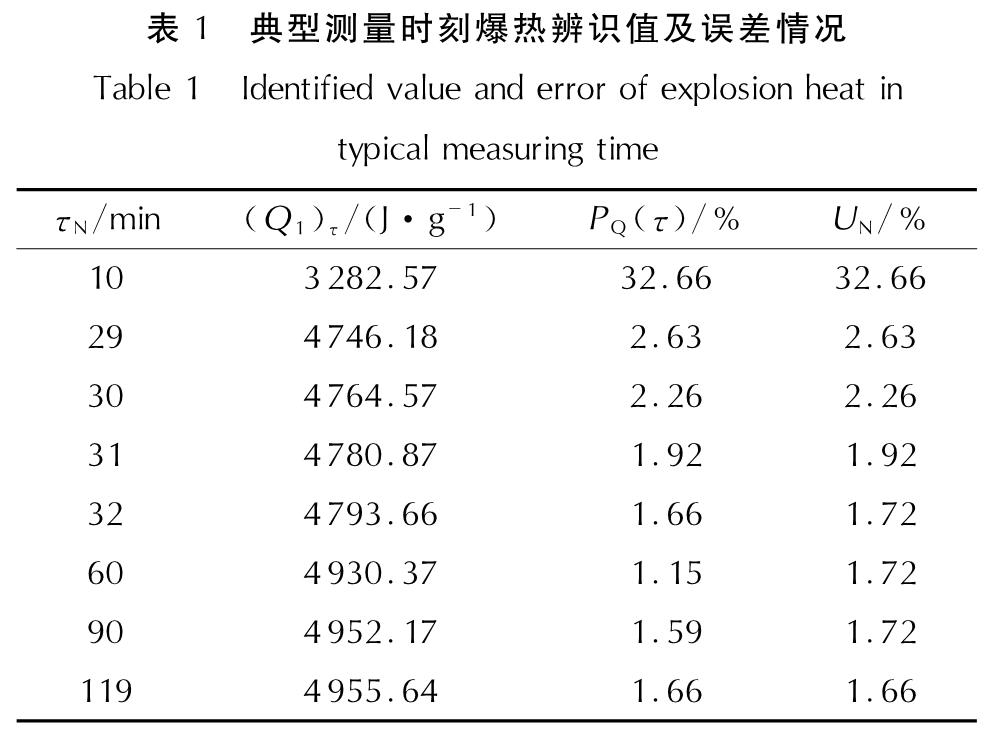
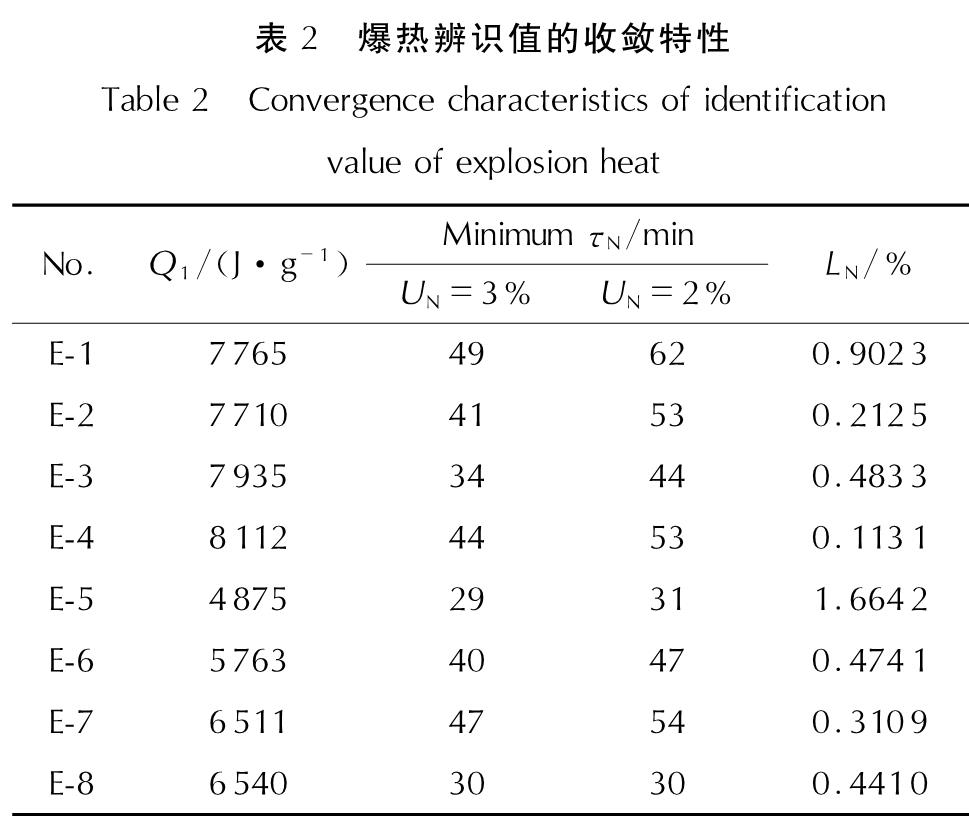
对爆热值为4000~9000J/g的8个典型样本进行了恒温法爆热测量,结果见表2。试验步骤参照国军标GJB772A-97中方法701.1爆热-恒温法,为减少随机误差,初期、主期、末期分别延长为21、100、20min,其他时间主要为温度调整时间,采样时间间隔为1min[9]。
定义测量时刻τ爆热辨识值相对误差为:
PQ(τ)=|(Q1-(Q1)τ)/(Q1)|(42)
式中:Q1为目标爆热值(这里取测量结束后经典法得到的爆热值),J/g;(Q1)τ为炸药爆热在测量时刻τ的系统辨识值,J/g。
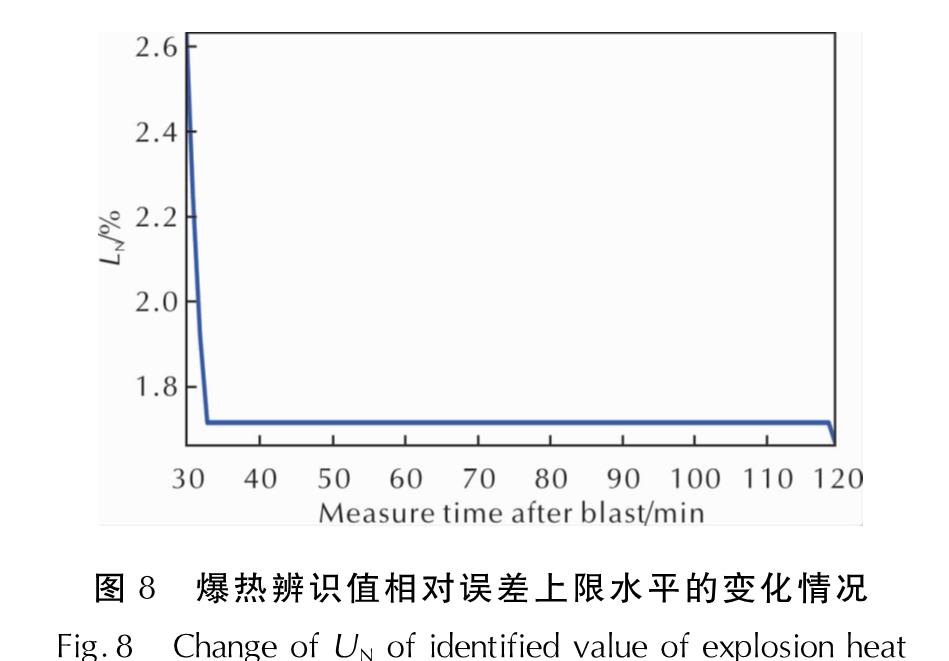
定义相对误差上限水平(记为UN)为起爆后测量时间τN之后的最大辨识相对误差; 定义极限收敛水平(记为LN)为相对误差上限水平的最小值。
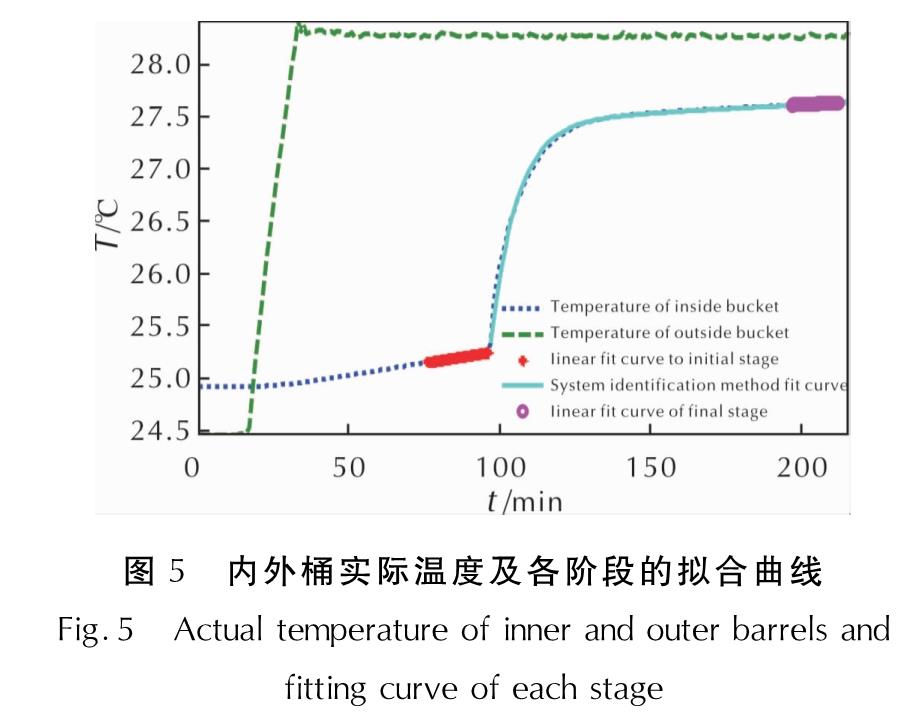
针对其中某次试验进行具体分析,内外桶温度及拟合温度随采样时间变化情况见图5。由图5可见,炸药起爆前的初期阶段与爆炸产物放热结束后的末期阶段,内桶水温度曲线具有极好的线性; 系统辨识法得到的整个主末期内桶水温度曲线具有极好的拟合度。
图5 内外桶实际温度及各阶段的拟合曲线
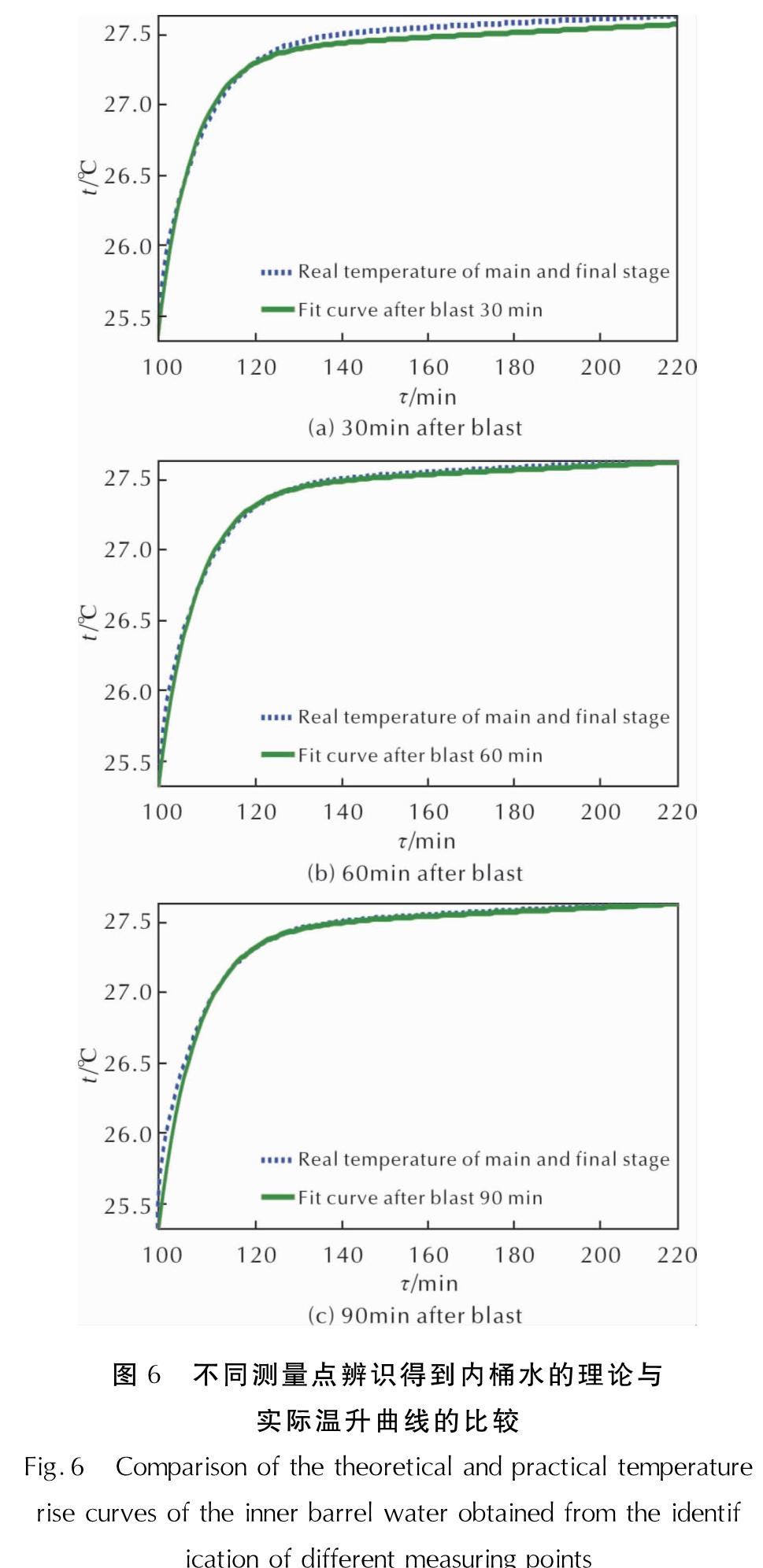
Fig.5 Actual temperature of inner and outer barrels and fitting curve of each stage为了检验系统辨识方法对内桶水长期温升的预测能力,取起爆后第30、60、90min时刻辨识得到的温度曲线参数,分别代入内桶水温升公式(13),得到拟合温升曲线与实际温升曲线,结果见图6。
从图6可知,当测量时间达到起爆后第60min时就可以相当精确地预测内桶水温的变化趋势。
图6 不同测量点辨识得到内桶水的理论与实际温升曲线的比较
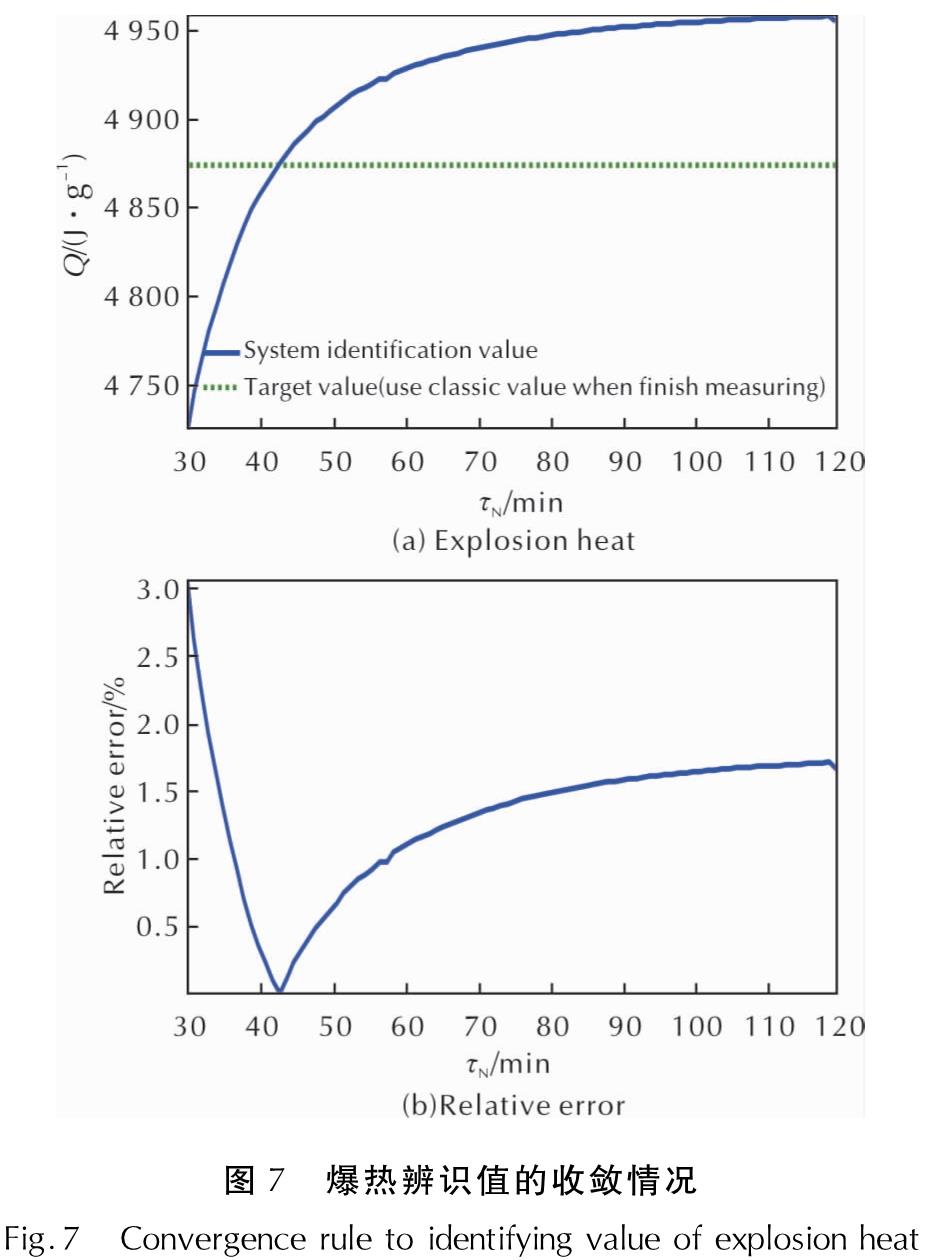
Fig.6 Comparison of the theoretical and practical temperature rise curves of the inner barrel water obtained from the identif ication of different measuring points爆热系统辨识仿真从起爆后第5min开始,取测量结束后用经典法计算得到的爆热值4874.52J/g作为目标值。仿真结果表明,爆热辨识值的相对误差随起爆后测量时间的增加而迅速减小,在起爆后第29min、31min分别收敛到了3%、2%的相对误差水平(对应爆热辨识值4746J/g、4781J/g),在第32min达到1.72%的相对误差水平后,相对误差在此误差水平内缓慢变化,并于第119min达到了1.66%的极限收敛水平,分别见表1、图7和图8。其中,图中时间从辨识误差第一次收敛至3%开始显示。
图8 爆热辨识值相对误差上限水平的变化情况
Fig.8 Change of UN of identified value of explosion heat为了验证本算法的普适性,试验选用了由HMX、Al粉、黏结剂等组成的E-1、E-2样本,由CL-20、AP、Al粉、黏结剂等组成的E-3、E-4样本,由TATB、Al粉、黏结剂等组成的E-5~E-8样本,针对8个典型样本利用稳健系统辨识方法得到爆热辨识值的收敛特性见表2。
由表2可见,爆热辨识值收敛至3%的相对误差水平测量时间不超过49min,收敛至2%的相对误差水平测量时间也不超过6min(约占主末期的1/2),其极限收敛水平均未超过2%,且大部分样本极限收敛水平未超过0.5%,充分说明了本算法的稳健性、精确性和快速性。
多次仿真表明,本方法得到的爆热辨识值相对误差近似按指数规律快速收敛至不超过3%的相对误差水平,然后在该范围内缓慢变化,收敛时间一般不超过主末期阶段的1/2,其辨识结果具有相当高的精度与可信度。而且,本算法辨识得到的中间参数kNW/(cNmN)可作为评判量热计的绝热性、一致性与稳定性等传热性能的重要依据。
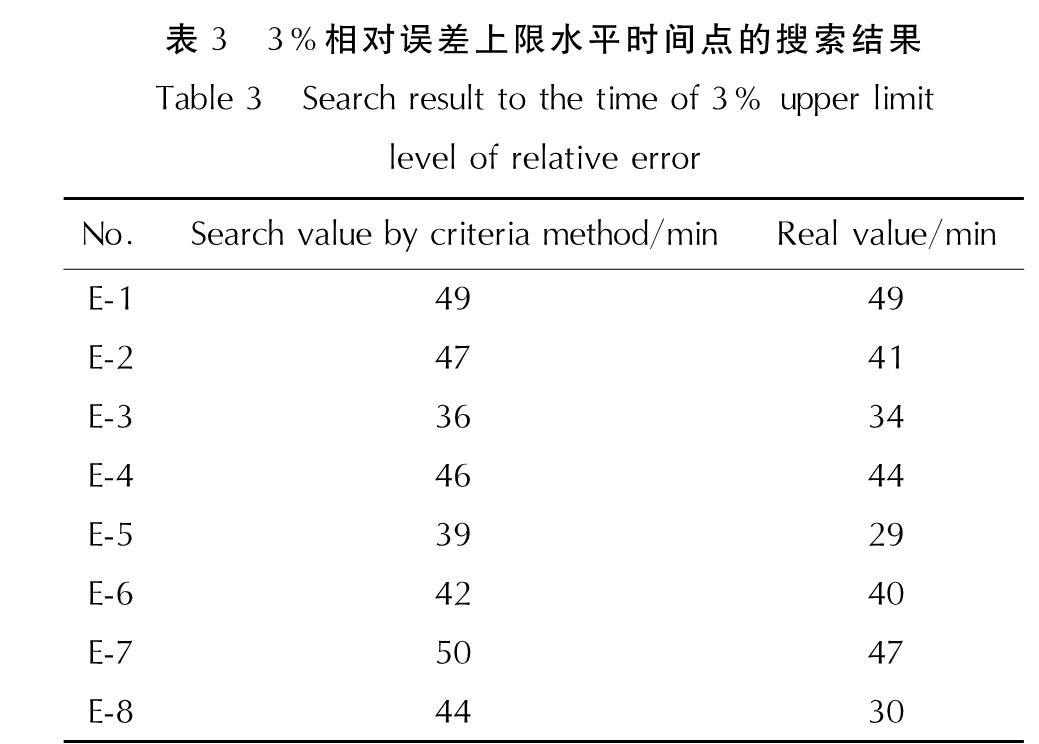
为了在实际测量中判断爆热辨识值的收敛时刻,本研究基于修正温升辨识值时间曲线在进入收敛阶段后具有波动小、变化慢的特点,在总结表2中8个样本的修正温升辨识值时间曲线数据的基础上,提出可供参考的爆热辨识值收敛时刻的试验判据法如下:对修正温升辨识时间曲线的时刻τJ及其前15min范围数据进行线性拟合,如果拟合得到的直线斜率绝对值不超过5.5×10-3℃/min,拟合残差均方根不超过6.0×10-3℃,则时刻τJ对应爆热辨识值相对误差上限水平不超过3%。
根据该试验判据,对表2中8个样本的修正温升辨识值曲线进行搜索,得到满足3%误差上限水平的第一个测量时刻数据见表3。
从表3可知,本研究提出的试验判据可有效指导实际测量中爆热辨识值收敛时间的判断,但由于该试验判据是基于小样本试验的统计结果,所以还需要在实践中完善。
4 结 论
(1)稳健辨识方法得到的爆热辨识值能在不超过主末期阶段1/2时间内快速、可靠性收敛至3%相对误差上限水平内,显著降低了因试验故障导致测量失败的风险。
(2)误差分析表明,爆热辨识值与经典法计算值的收敛值相等,即系统辨识方法与经典方法理论上具有相同的测量精度; 虽然量热计测爆热的传热学模型基于“炸药产热是瞬态过程”的假设建立,但氧化、燃烧等非瞬态产热过程对模型造成的偏移是可以忽略的,因此,本方法是足够稳健的。
(3)本研究提出的收敛时间试验判据能可靠地判断爆热辨识值的收敛时间,但由于该试验判据是基于小样本试验的统计值,所以还需要在实践中完善。本方法还可应用于爆热预估、内桶水温升趋势预测、故障诊断等领域,是恒温法爆热测量经典方法的有益补充。
炸药爆热系统辨识的基本思路是:首先,根据初期阶段内桶水温度曲线辨识出参数kNW/(cNmN),然后根据主期与末期阶段内桶水温度曲线辨识出参数u1、λ1、λ2。再根据中间参数kNW/(cNmN)、u1、λ1、λ2辨识得到TE(τM)、kNZ/cNmN、kNZ/cZmZ等3个目标参数。最后,根据目标参数辨识得到内桶水的修正温升,再结合经典爆热计算公式(3)得到炸药的爆热计算结果。
2.1 初期阶段的参数辨识由于内外桶绝热良好,内桶系统的比热容与质量的乘积是一个非常大的值,则:
0<(kNW)/(cNmN)1(18)
根据泰勒展开公式,内桶水温度曲线(见式(12))在整个初期阶段具有较好的线性,即:
T⌒I(τ)≈(kNW)/(cNmN)(TW-TI(τS)+TC)τ+TI(τS)-
(kNW)/(cNmN)(TW-TI(τS)+TC)τS(19)
初期阶段由于炸药未点火,如出现系统故障,量热计尚可调整与修复。因此,认为初期阶段的数据可全部利用。基于初期阶段内桶水温度采样数据进行线性拟合得到:
TI(τ)=kS1τ+kS2+ε(τ)(20)
式中:kS1、kS2分别为拟合得到的一次项与零次项系数; ε(τ)为拟合残差。
比较式(19)与式(20)可得到中间参数kNW/(cNmN)的辨识结果为:
(kNW)/(cNmN)=(kS1)/(TW+TC-kS1τS-kS2)(21)
2.2 主期与末期阶段的参数辨识主期与末期阶段由于炸药已点火,如出现系统故障,量热计调整修复难度很大,后续测量数据面临不可信甚至丢失的风险。
针对这一情况,采用曲线拟合思想,基于起爆至测量时间τ的内桶水温度数据辨识参数u1、λ1、λ2的目标函数为:
f(u1,λ1,λ2)=∑kj=1[T⌒I(τj)-TI(τj)]2(22)
式中:T⌒I(τj)、TI(τj)分别为在第j个采样时间点τj处内桶水的理论温度(见式(13))与实际测量温度,k为炸药点火至采样时间点τj的采样点个数。
根据式(15)可知,kNW/(cNmN)近似为0时,λ1也十分接近0。即λ1反映的是内桶水温的慢变过程,但慢变趋势通常不显著,易被快变过程与随机扰动干扰,进而造成λ1的辨识值出现较大误差,使得λ1的辨识值向真实值收敛速度很慢。多次仿真表明,如不对λ1进行约束,当测量时间较短时,λ1的辨识值对温度长期的慢变过程预测能力很差。因此,为防止λ1陷入局部最优解,加快收敛速度,求解目标函数式(22)最小值时,需对λ1进行约束。
综合式(15)与式(18)分析可得:
λ1≈-(kNW)/(cZmZ+cNmN)+((cZmZ)2cNmN)/((cZmZ+cNmN)3)(kNW)/(kNZ)(kNW)/(cNmN)(23)
考虑到kNZkNW、cNmNcZmZ,以及kNW/(cNmN)本身的辨识误差,结合式(23),本研究给中间参数λ1的约束条件为:
-(kNW)/(cNmN)≤λ1≤-0.9(kNW)/(cNmN)(24)
利用最优化方法求解有约束条件式(24)的目标函数f(u1,λ1,λ2)的最小值,即可辨识得到测量时间τ对应的中间参数u1、λ1、λ2。然后,根据式(14)~式(17)可得TE(τM)、kNZ/cNmN、kNZ/cZmZ等3个目标参数在测量时间τ的辨识方法见式(25):
{((kNZ)/(cZmZ))τ=((λ1)τ(λ2)τ)/( kNW/cNmN)
((kNZ)/(cNmN))τ=-[(λ1)τ+(λ2)τ+((λ1)τ(λ2)τ)/(kNW/cNmN)+(kNW)/(cNmN)]
(TE(τM))τ=((TW+TC)kNW/cNmN+(λ1)τTI(τM))/(kNW/cNmN+(λ1)τ)
-([(λ1)τ-(λ2)τ](u1)τkNW/cNmN)/([kNW/cNmN+(λ1)τ][kNW/cNmN+(λ2)τ])(25)
式中:(λ1)τ表示参数λ1在时刻τ的系统辨识值; 依此类推,其他参数若由小括号及τ的下标构成,则表示该参数在τ时刻的系统辨识值。
2.3 炸药爆热的计算解算主期与末期阶段的传热学方程(11)得到爆炸产物向内桶系统传热量时间函数QN1(τ),可证明,测量时间无限长时,有:
QN1(+∞)=cZmZ(TE(τM)-TC-TW)(26)
根据修正温升的定义可知,内桶水修正温升在测量时刻τ的辨识方法为:
(ΔtS)τ=(QN1(+∞))/(cNmN)=(cZmZ)/(cNmN)(TE(τM)-TC-TW)≈
((kNZ/cNmN)τ)/((kNZ/cZmZ)τ)((TE(τM))τ-TC-TW)(27)
因此,代入式(25)目标参数TE(τM)、kNZ/cNmN、kNZ/cZmZ在时刻τ的辨识值,即可得到内桶水在测量时间τ的修正温升,再根据公式(3)即可计算得到炸药爆热。
2.4 辨识误差分析2.4.1 收敛精度分析分别将初期阶段、主期与末期阶段传热学方程解算得到的内桶水温度曲线T⌒I(τ),代入经典爆热计算公式(1)、(2),可以证明:经典算法中内桶的修正温升收敛为:
ΔtJ=(cZmZ)/(cNmN)(TE(τM)-TC-TW)(28)
比较式(28)与式(27)可知,稳健系统辨识方法与经典方法得到的内桶水的修正温升理论值相同,因此爆热理论值也相同。
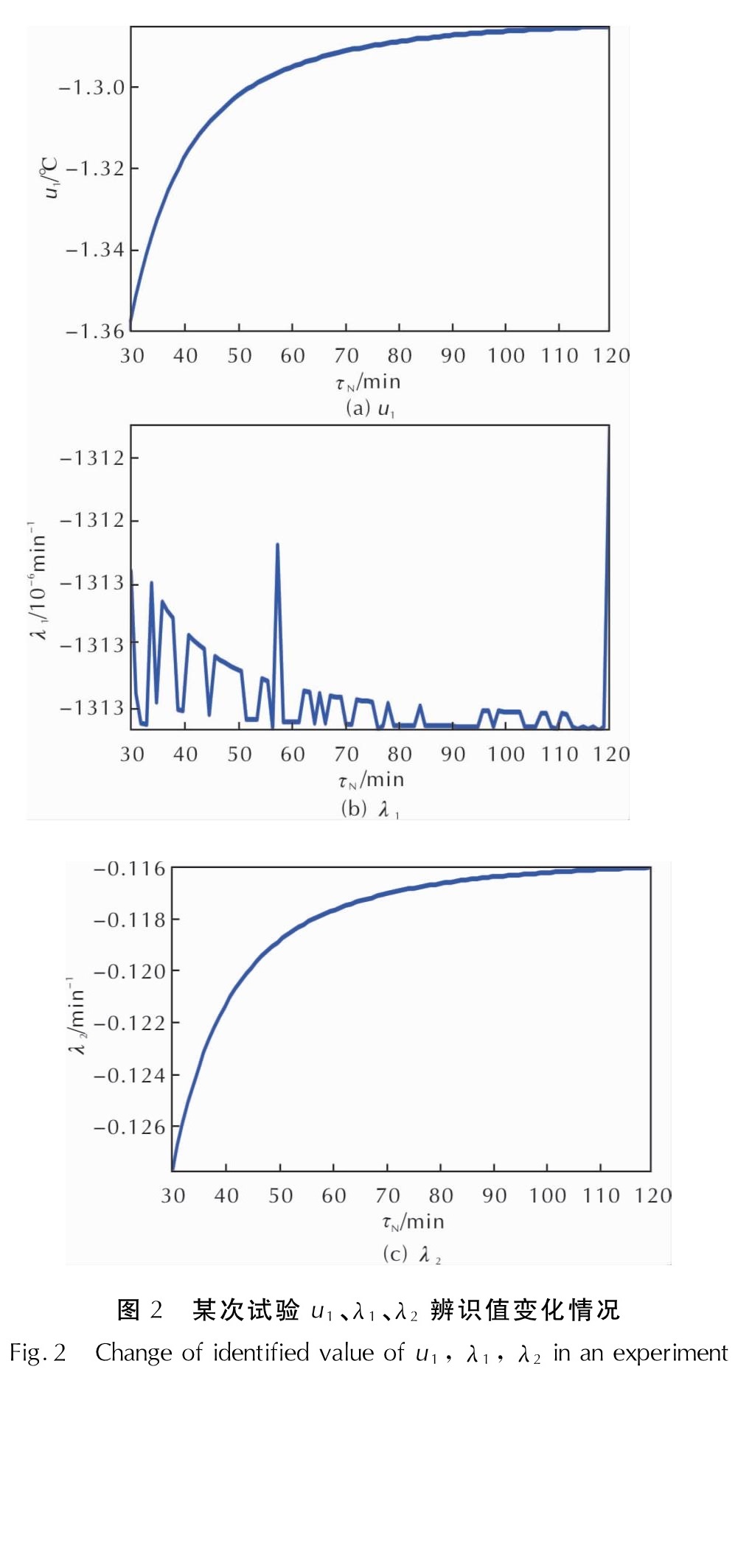
2.4.2 收敛稳健性分析中间参数u1、λ2辨识值较大,收敛比较稳定; λ1辨识值近似为0,虽然通过约束式(24)提高了对温度慢变项的长期预测精度,但温度随机扰动与快变项的干扰易引起λ1辨识值振荡,见图2。图中
τN表示以炸药起爆为计时零点的测量时间。因此,本节主要分析λ1辨识结果对各参数辨识误差的影响。
图2 某次试验u1、λ1、λ2辨识值变化情况
Fig.2 Change of identified value of u1, λ1, λ2 in an experiment将λ1在测量时刻τ的辨识值表示为:
(λ1)τ=(-1+δτ)((kNW)/(cNmN))(29)
根据式(24)可知,δτ的值域为[0,0.1]。将式(29)代入式(25)可得:
{((kNZ)/(cZmZ))τ=(-1+δτ)(λ2)τ
((kNZ)/(cNmN))τ=-δτ((kNW)/(cNmN)+(λ2)τ)
(TE(τM))τ=((u1)τ+TW-TI(τM)+TC)/(δτ)+
TI(τM)-(kNW/(cNmN))/(kNW/(cNmN)+(λ2)τ)(u1)τ
(ΔtS)τ=(δτ)/(1-δτ)(u1)τ+(TW+TC-
TI(τM)+(u1)τ)(1/((λ2)τ)(kNW)/(cNmN)+1)(30)
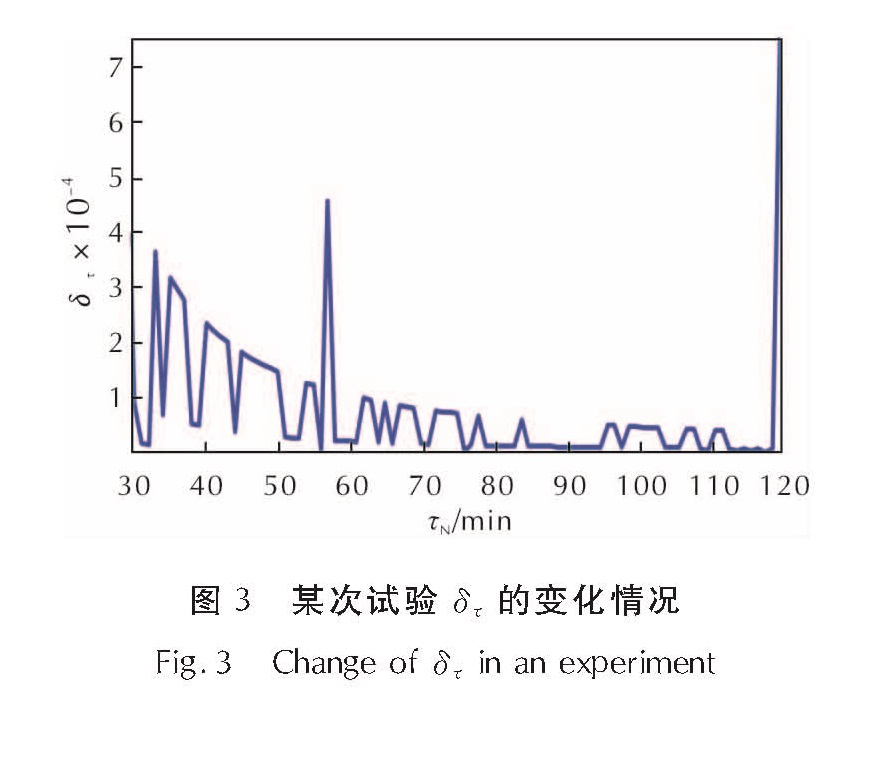
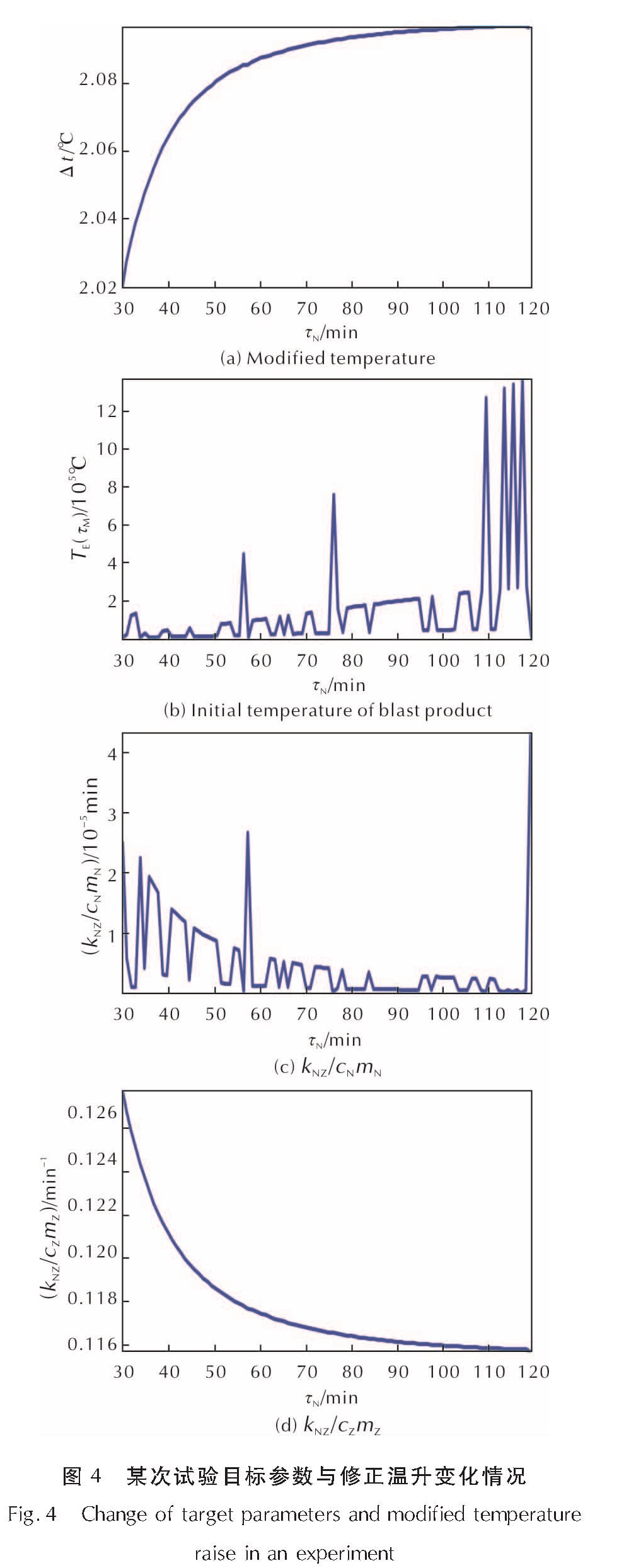
模拟结果表明,δτ大部分辨识时间计算结果在10-6至10-3范围内,但收敛较差,即使爆热辨识值已收敛至3%误差范围内,δτ也常常出现剧烈振荡,最大值与最小值相差也通常可达数百倍,见图3。图4为目标参数与修正温升变化情况。
图3 某次试验δτ的变化情况
Fig.3 Change of δτ in an experiment图4 某次试验目标参数与修正温升变化情况
Fig.4 Change of target parameters and modified temperature raise in an experiment根据这些特点,结合式(23)、式(29)、式(30),可得到如下结论:
(1)目标参数TE(τM)、kNZ/cNmN对λ1辨识值微小波动异常敏感,见图4。δτ的剧烈振荡致其难以收敛,其辨识结果也不可信。
(2)由于δτ很小,内桶水修正温升ΔtS与kNZ/cZmZ的辨识值具有较快的收敛速度、较高的辨识精度以及较好的可信度,见图4。再比较式(28)与式(27)可知,爆热辨识值理论上收敛于经典值,因此,本算法是稳健的。
(3)中间参数λ1的辨识值近似收敛于kNW/(cNmN),因此,增加约束条件(24)虽会出现λ1辨识值小幅振荡的现象,却有利于爆热计算值的快速收敛。
(4)从减少辨识误差的角度讲,增大外桶对内桶传热的影响,即增大kNW/(cNmN)有利于提高λ1的辨识精度,并减少温度扰动的影响,但外桶温度的波动将会影响到内桶温度,这显然是得不偿失的。
(5)从故障诊断角度讲,如果辨识得到的参数kNW/(cNmN)或λ1较大,则说明外桶至内桶的绝热性能下降或故障,因此,本方法也具有对量热计进行故障诊断的能力。
2.5 模型误差分析由于非理想炸药爆轰后存在金属粉氧化的二次反应,以及在含氧气环境下的燃烧反应,而氧化/燃烧时间要远大于爆轰时间,与本研究模型的瞬态假设存在一定的偏离。因此需要分析非理想炸药爆轰后燃烧/氧化产热对辨识误差的影响。考虑燃烧/氧化产热影响后,式(10)变为:
QN1(τ)=QB(τ)+cZmZ(TBE(τM)-TE(τ))(31)
式中:TBE(τM)为炸药爆轰后产物的温度; QB(τ)为燃烧/氧化反应在τM至τ时段产热量。
如果可燃物的消耗速率是先快后慢,则更有利于模型关于反应过程是瞬态的假设,为了最大化地分析模型误差,这里给出不利于瞬态性的假设,即:可燃物的消耗是匀速的,因此,有:
QB(τ)={QAB(τ-τM)/τB τM≤τ≤τM+τB
QAB τ>τM+τB(32)
式中:QAB为总的燃烧/氧化产热量; τB为燃烧/氧化产热总时间。
为了与瞬态模型的总产热量对应,得到总的燃烧/氧化产热量为:
QAB=cZmZ(TE(τM)-TBE(τM))(33)
由于燃烧/氧化时间较短,而搅拌产热与外桶传热速率较慢,因此,结合式(4)、式(31)、式(32)、式(9),并忽略搅拌产热与外桶传热的影响,可得燃烧/氧化阶段爆炸产物向内桶系统的传热方程为:
(dQN1(τ))/(dτ)=-kZT(1/(cZmZ)+1/(cNmN))QN1(τ)+
(kZTQABτ)/(cZmZτB)+kZT(TBE(τM)-TI(τM))(34)
结合式(33),解算式(34)可知,如果
kNZ(1/(cZmZ)+1/(cNmN))τB≈0(35)
则燃烧/氧化阶段结束时,爆炸产物与内桶水的温度近似解为:
{TE(τM+τB)≈TE(τM)-(TBE(τM)-TI(τM))(kNZτB)/(cZmZ)
TI(τM+τB)≈TI(τM)+(TBE(τM)-TI(τM))(kNZτB)/(cNmN)(36)
根据文献[11]中TNT炸药在纯氧环境爆轰试验温度曲线可知,炸药燃烧/氧化时间不超过1/30min,结合前文kNZ/cZmZ、kNZ/cNmN的辨识情况来看,式(35)是成立的。
燃烧/氧化阶段结束后的传热模型与瞬态过程的传热模型是一致的,只是初始状态变为式(36),因此,解算得到燃烧/氧化阶段结束后内桶水的温升曲线为:
T⌒IB(τ)=TW+TC+uBexp(λ1(τ-(τM+τB)))+
(TI(τM+τB)-TC-TW-uB)exp(λ2(τ-(τM+τB)))(37)
式中:λ1、λ2、Δ的取值与式(15)、式(16)、式(17)相同。
uB=((TE(τM+τB)-TI(τM+τB))(kNZ)/(cNmN))/((Δ)1/2)-
((TW+TC-TI(τM+τB))((kNZ-kNW)/(cNmN)+(kNZ)/(cZmZ)+(Δ)1/2))/(2(Δ)1/2)(38)
为了与瞬态模型中内桶水温升表达式对应,将式(37)改写为:
T⌒IB(τ)=TW+TC+u1Bexp(λ1(τ-τM))+
(TBI(τM)-TC-TW-u1B)exp(λ2(τ-τM))(39)
对比瞬态模型式(13)与燃烧/氧化模型式(37),再结合cZmZcNmN,kNWkNZ,可得式(39)中的参数为:
{u1B≈u1-(kNW)/(cNmN)τB(ΔTA-ΔTF)
TBI(τM)≈TI(τM)-(kNZ)/(cZmZ)τBΔTF(40)
式中:ΔTA表示试验预设温升; ΔTF表示燃烧/氧化引起的修正温升,且有:
{ΔTA=TW+TC-TI(τM)
ΔTF=cZmZ(TE(τM)-TBE(τM))/cNmN(41)
式(40)表明匀速燃烧/氧化模型相对于瞬态模型的参数偏移量。为了说明参数偏移量的上限,这里假设炸药产热过程全部为匀速燃烧/氧化过程,燃烧/氧化时间τB=1/30min,根据表2中8个样本的辨识情况计算得到u1的最大偏移量为1.54×10-4℃,TI(τM)的最大偏移量为1.59×10-2℃。可见,即使在最差的假设条件下,模型误差造成的参数偏移量也是可以忽略不计的,因此,本算法是足够稳健的,可以满足无氧/有氧环境下的爆热测量精度要求。
- [1] 王晓峰,冯晓军,肖奇.温压炸药爆炸能量的测量方法[J].火炸药学报,2013,36(2):9-12.
- [2]国防科学技术工业委员会. GJB 772.303-90炸药试验方法-爆热测定[S]. 1990.
- [3]曹威,何中其,陈网桦,等.水下爆炸法测量含铝炸药后燃效应[J].含能材料, 2012, 20(2): 229-233.
- [4]SAMUEL P H, RICARDO I. Predicting heats of explosion of nitrate esters through their NBO charges and 15N NMR chemical shifts on the nitro groups[J].Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2010(10):279-283.
- [5]MOHAMMAD, HOSSEIN, KESHAVARZ. Quick estimation of heats of detonation of aromatic energetic compounds from structural parameters[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006(9): 549-554.
- [6]王建灵,李正来,王青枝.绝热式炸药爆热热量计绝热性能的测定方法[J]. 火炸药学报, 2007,30(2): 52 -58.
- [7]姜炯,贾丁海.BR-1型绝热式爆热测量系统的研究[J].矿冶工程,1984,9(4):4-8.
- [8]卢洪义,杨兴根.固体推进剂高精度爆热测试系统设计[J].自动化与仪器仪表,1999(8):35-37.
- [9]范荣桂.炸药爆热的恒温法测试研究[J].煤矿爆破,2001(4):9-11.
- [10]杨世铭, 陶文铨.传热学[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社, 2006.
- [11]金朋刚, 郭炜, 任松涛, 等. TNT密闭环境中能量释放特性研究[J]. 爆破器材, 2013, 43(2):10-14.