2.1 形貌分析(SEM)
原料CL-20、原料TKX-50和CL-20/TKX-50共晶的SEM图如图2所示。
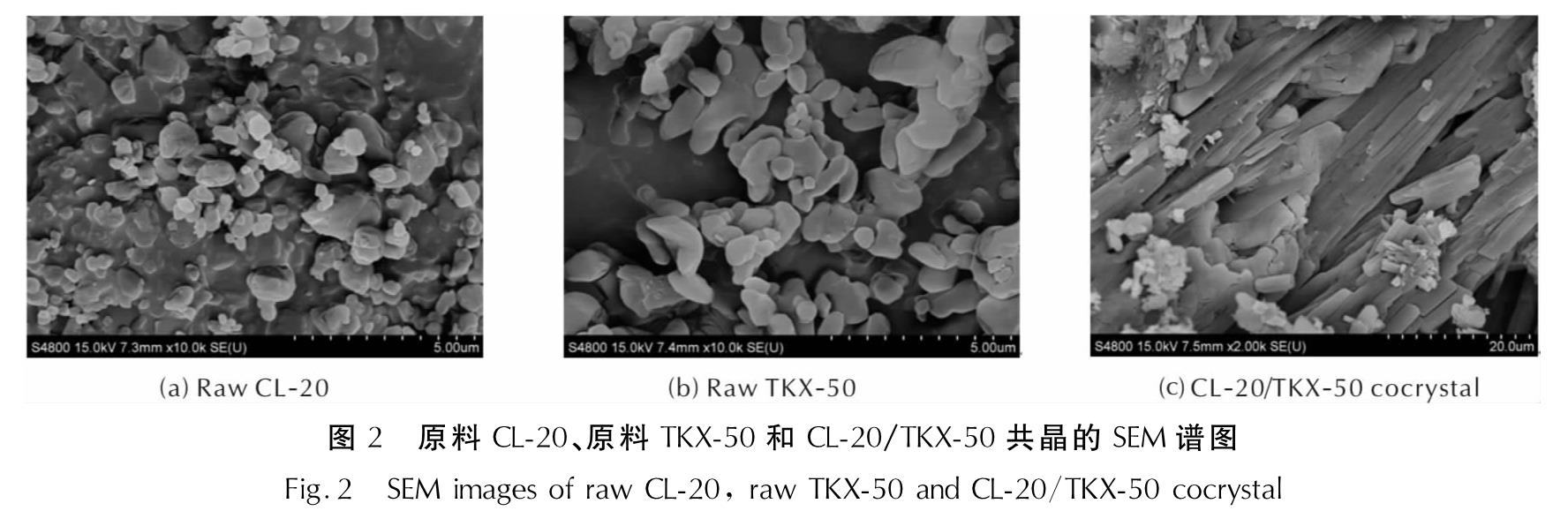
由图2可看出,原料CL-20和原料TKX-50晶体形貌为近球形,且粒度分布较为均匀,粒径约为1μm; CL-20/TKX-50共晶的形貌则呈现出细长片状的结构,这与前两者的特征截然不同,粒度分析发现共晶的粒度约10μm。共晶过程改变了原有晶体的形貌特征,同时也可证明新的晶体生成。
图2 原料CL-20、原料TKX-50和CL-20/TKX-50共晶的SEM谱图
Fig.2 SEM images of raw CL-20, raw TKX-50 and CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal
2.2 粉末X射线衍射分析(XRD)
对原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50混合物以及CL-20/TKX-50共晶分别进行XRD测试,结果如图3所示。
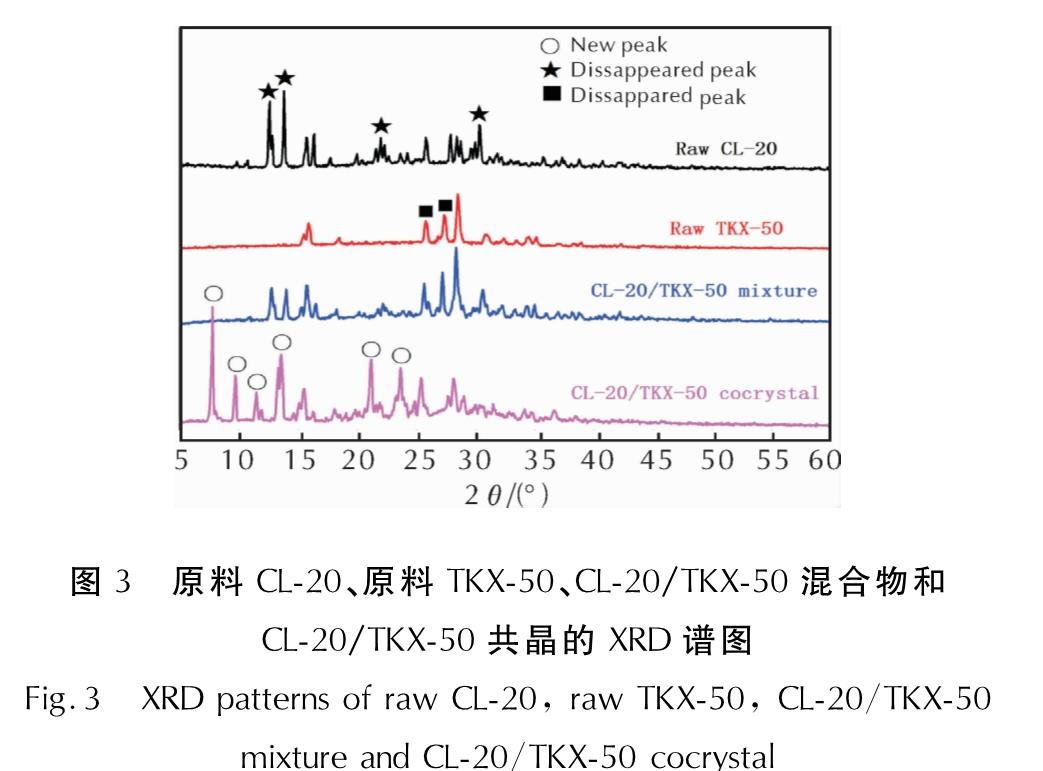
图3 原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50混合物和CL-20/TKX-50共晶的XRD谱图
Fig.3 XRD patterns of raw CL-20, raw TKX-50, CL-20/TKX-50 mixture and CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal
由图3可看出,TKX-50/CL-20混合物的衍射图中具有原料TKX-50和CL-20的所有特征衍射峰。TKX-50/CL-20共晶在7.8°、9.7°、11.5°、13.5°、21.2°、23.7°出现了新的衍射峰,这是单一组分原料CL-20和TKX-50所没有的。同时,原料CL-20在12.6°、13.7°、21.9°、30.2°的特征峰,原料TKX-50在25.8°和27.3°处的特征峰在CL-20/TKX-50共晶的衍射峰中均消失。此外,根据文献[17-19]可知,CL-20/TKX-50共晶的XRD特征峰与原料CL-20可能具有的其他晶型的特征峰也均有明显不同。因此,通过XRD测试可以对所制备的共晶和原材料CL-20与TKX-50进行区分,这也说明共晶的形成改变了晶体内部结构的对称性,表明形成了一种新的晶格结构。
2.3 红外光谱分析(IR)
原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50混合物以及CL-20/TKX-50共晶的傅里叶红外光谱如图4所示。
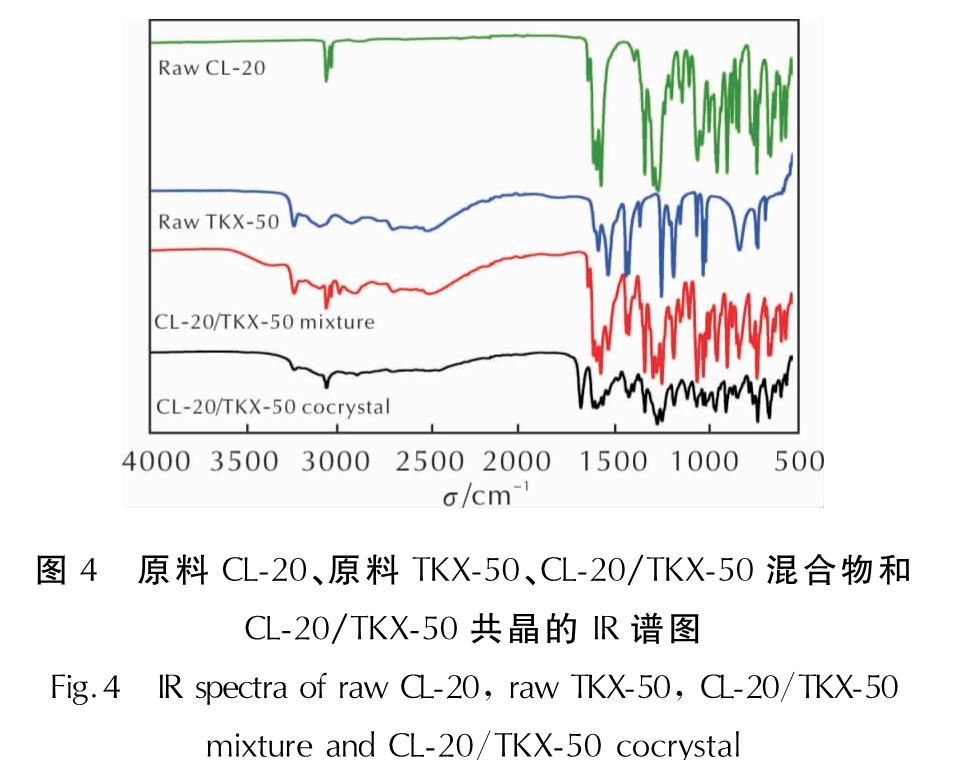
图4 原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50混合物和CL-20/TKX-50共晶的IR谱图
Fig.4 IR spectra of raw CL-20, raw TKX-50, CL-20/TKX-50 mixture and CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal
由图4可看出,在共晶和混合物的谱图中都可以观察到原料CL-20和TKX-50的主要吸收峰。同时,CL-20和TKX-50的一些主要吸收峰在共晶的谱图中体现为向高波数或低波数的方向发生了偏移。而混合物的谱图则仅仅体现为CL-20与TKX-50两种原料谱图的重叠。例如,原料CL-20中3016.8cm-1处的C—H伸缩振动,在共晶中偏移至3044.0cm-1处; 1602.3、1632.2cm-1处的—NO2反对称伸缩振动,在共晶中分别偏移至1604.2、1670.7cm-1处; 1382.5cm-1处的C—H弯曲振动,在共晶中偏移至1386.5cm-1。同时,原料TKX-50中位于3078.0cm-1处的N—H伸缩振动,在共晶中偏移至3044.0cm-1处; 1523.1cm-1处的N—H弯曲振动,在共晶中偏移至1551.7cm-1处,1235.8、1170.7cm-1处的C—N伸缩振动,在共晶中分别偏移至1233.2和1167.9cm-1处。此外,在854.5cm-1处(CL-20的C—C伸缩振动)、1602.4cm-1(CL-20的—NO2伸缩振动)、1523.1~1576.6cm-1(TKX-50中—NH+3弯曲振动)在共晶中均发生了削弱或偏移。
CL-20/TKX-50混合物的红外谱图和共晶的红外谱图具有明显的差异。吸收峰位置的偏移和强度的改变说明两种分子间发生了一定的相互作用。分析推测为CL-20中的—NO2和TKX-50中的—NH+3之间形成了氢键。
2.4 拉曼光谱分析(Raman)
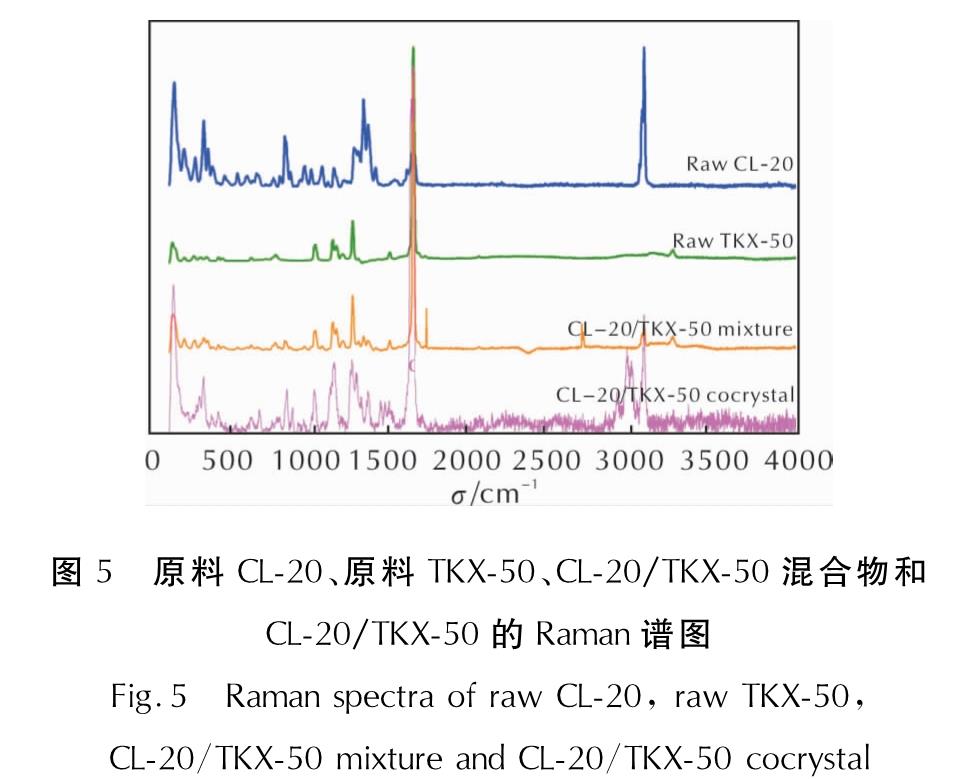
原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50混合物以及CL-20/TKX-50共晶的拉曼光谱如图5所示。
图5 原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50混合物和CL-20/TKX-50的Raman谱图
Fig.5 Raman spectra of raw CL-20, raw TKX-50, CL-20/TKX-50 mixture and CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal
由图5可以看出,原料CL-20在819.1、981.0、1305.7cm-1处有振动带,这些振动带在共晶光谱中分别偏移到833.7、1001.8、1331.4cm-1处。同时,TKX-50在762.1、1006.4、1114.7cm-1处的振动带偏移到了769.5、1002.7、1125.8cm-1处。从图5中也可以看出,共晶和混合物的谱图有着明显的差异,混合物的谱图总体体现为原料谱图的简单重合,混合物在819.1cm-1和1114.7cm-1处的振动带在共晶中偏移到833.7cm-1和1125.8cm-1处。这些改变都可以归结为CL-20中的—NO2和TKX-50中的—NH+3之间形成了氢键,这些氢键的存在促进了共晶的形成。
2.5 热分析(DSC)
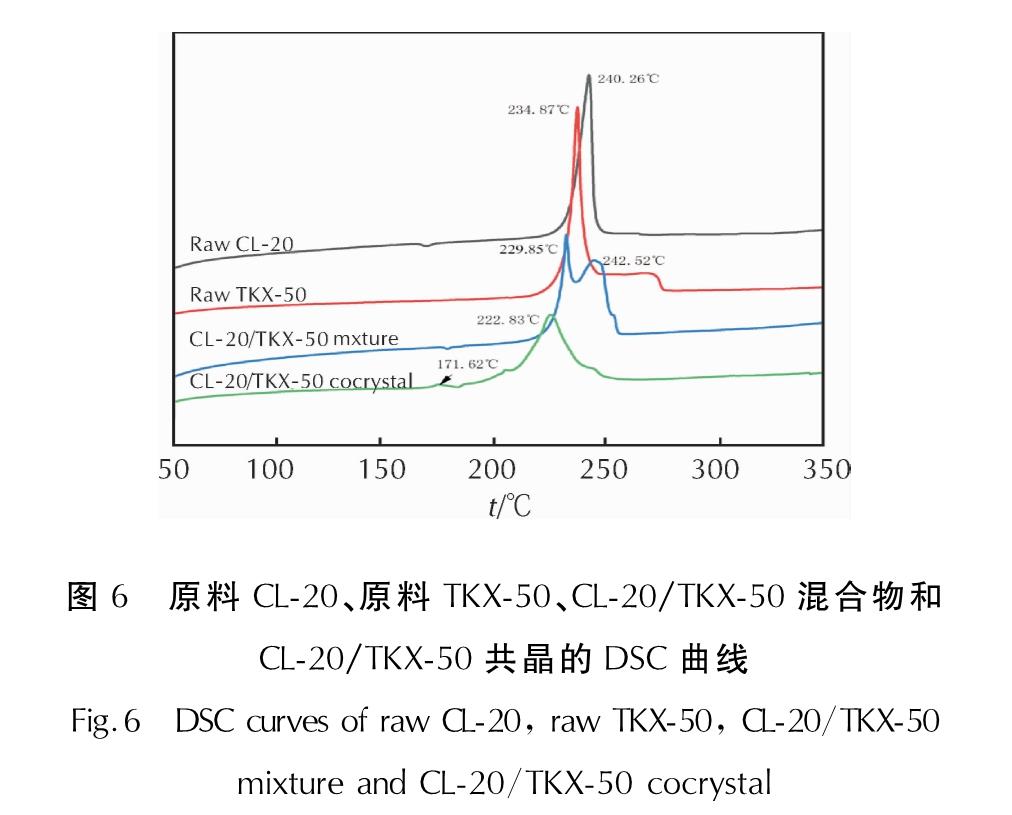
升温速率8℃/min条件下,原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50混合物和CL-20/TKX-50共晶的DSC曲线如图6所示。
图6 原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50混合物和CL-20/TKX-50共晶的DSC曲线
Fig.6 DSC curves of raw CL-20, raw TKX-50, CL-20/TKX-50 mixture and CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal
由图6可看出,原料CL-20、原料TKX-50的放热分解峰分别出现在240.2、234.8℃。CL-20/TKX-50混合物的分解过程明显是CL-20和TKX-50热分解的简单叠加,存在两个放热分解峰:第一个峰出现在229.8℃,对应的是部分TKX-50放热分解; 第二个峰出现在242.5℃,对应的是CL-20发生放热分解。从分解曲线中可以看出,CL-20/TKX-50共晶的热分解行为与原料CL-20、原料TKX-50和CL-20/TKX-50混合物有着明显的不同。随着温度的不断升高,CL-20/TKX-50共晶的热分解曲线在171.6℃出现第一个强度较小的放热分解峰,这可归因为共晶结构中的氢键遭到破坏,少量的TKX-50开始发生分解; 随后,大量共晶物质开始发生分解并在222.8℃出现第二个放热分解峰。这些明显差异说明CL-20/TKX-50共晶分子间氢键的形成与新结构的存在,再次证明CL-20/TKX-50共晶的形成。
2.6 撞击感度与爆速、爆压预测
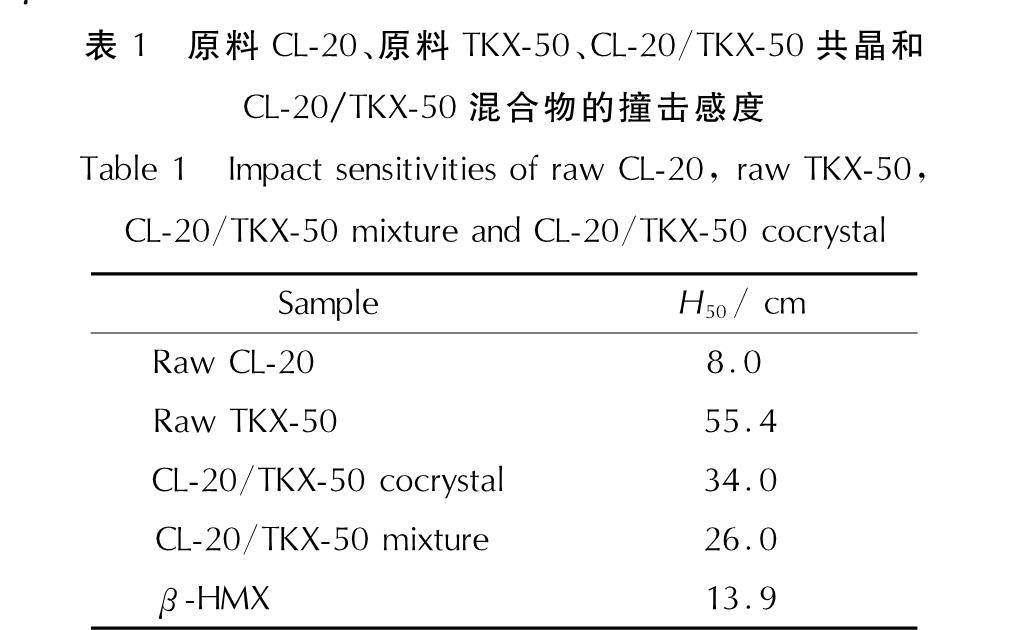
对原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50混合物和CL-20/TKX-50共晶进行撞击感度测试,并与β-HMX进行对比,结果如表1所示。
表1 原料CL-20、原料TKX-50、CL-20/TKX-50共晶和CL-20/TKX-50混合物的撞击感度
Table 1 Impact sensitivities of raw CL-20, raw TKX-50, CL-20/TKX-50 mixture and CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal Sample H50/ cmRaw CL-20 8.0 Raw TKX-50 55.4CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal 34.0CL-20/TKX-50 mixture 26.0β-HMX 13.9
从表1可以看出,CL-20/TKX-50共晶的特性落高低于原料TKX-50,但明显高于原料CL-20和β-HMX,也明显高于CL-20/TKX-50混合物的感度,说明与原料CL-20和β-HMX相比,溶剂-非溶剂法制备的CL-20/TKX-50共晶撞击感度更低。因此,将低感度的TKX-50用作配体与高感度的CL-20制备共晶能够有效降低CL-20的感度。
根据共晶形成的机理可知,共晶物质可以推测是两种分子利用氢键等作用以摩尔比1:2结合在同一晶胞里。根据Brinkley-XWilson规则,得到CL-20/TKX-50共晶的爆炸反应方程式:
C10H22N32O20——11H2O+9CO+C+16N2
理论爆速可以根据以下公式预测:
F=(100*[nO+nN-(nH)/(2nO)+A/3-(nB)/(1.75)-(nC)/(2.5)-(nD)/4-(nE)/5])/M-G
D=(F-0.26)/(0.55)
Pc-j=ρ0D2(1-0.713ρ0.070)
其中:F表示爆轰因子; nO、nN、nH表示分子中氧、氮、氢原子的个数; 芳香族化合物A=1,否则A=0; nB表示生成H2O和CO2后剩余的O原子的数目; nC表示O〖FY=,*2〗C双键的个数; nD表示C—XO单键的个数; nE表示硝基脂或硝酸盐中NO2的个数; M为炸药的分子质量; 对于固体炸药G=0,液体炸药G=0.4; Pc-j为气体产物的爆压, GPa; ρ0为炸药密度, g/cm3; D为爆速, km/s。
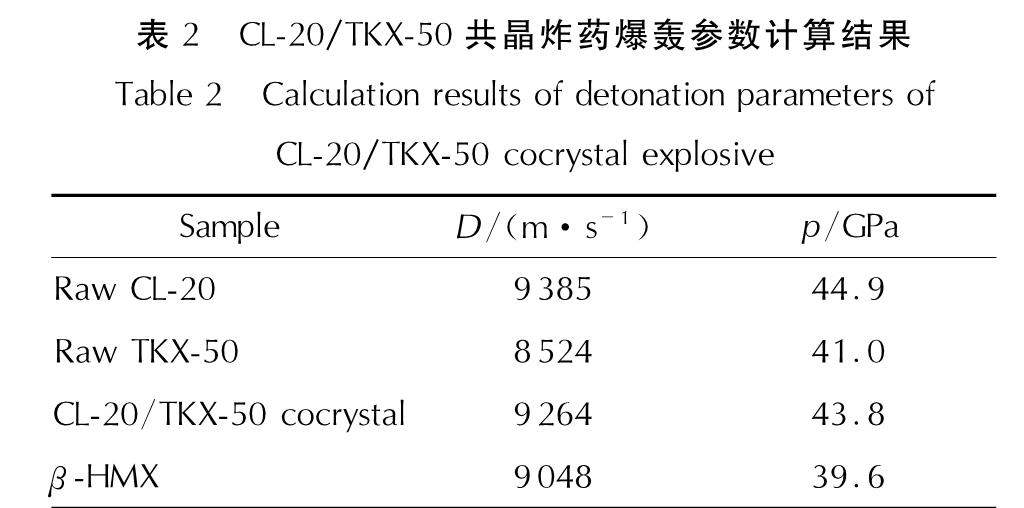
CL-20/TKX-50共晶的爆速和爆压计算结果见表2。
表2 CL-20/TKX-50共晶炸药爆轰参数计算结果
Table 2 Calculation results of detonation parameters of CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal explosive Sample D/(m·s-1)p/GPaRaw CL-20 9385 44.9Raw TKX-50 8524 41.0CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal 9264 43.8β-HMX 9048 39.6
从表2可以看出,CL-20/TKX-50共晶在具有较低机械感度的同时保持了较好的爆轰性能,爆速和爆压较CL-20略微下降,但和β-HMX相比,爆轰性能有着较为明显的提高。尽管计算结果与实际测试结果有一定的误差,但这也能充分说明CL-20/TKX-50共晶具有良好的爆轰性能。CL-20/TKX-50共晶炸药有望成为替代CL-20的新兴优质炸药。
2.7 共晶形成机理讨论
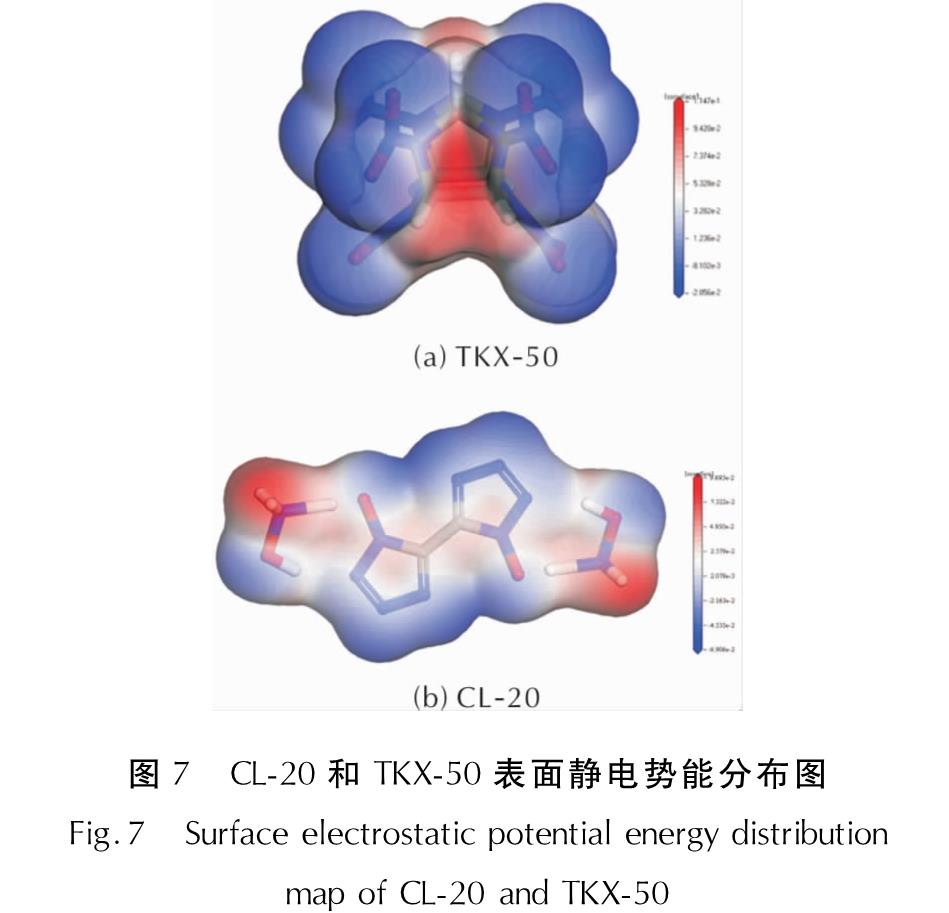
CL-20是一种结构复杂的笼状化合物,可以看作是一个六元环和两个五元环环状排列在一起的结构。CL-20分子结构上具有六个硝基基团,TKX-50是一种离子盐结构,具有两个羟胺阳离子。分子表面静电势直接影响着分子的物理与化学性质,包括:能量、共价键和离子键半径、电负性(化学势能)和一系列基于非共价相互作用的性能。因此,对CL-20和TKX-50进行表面静电势能分析有助于探讨CL-20/TKX-50共晶的形成机理。
静电势能是分子间非共价键作用形成的最主要因素。因此,用Materials Studio 5.0软件DMol3模块,采用泛函为GGA-XBLYP,任务为Geometry Optimization,所选的性质项为Electron density和Electrostatics,分析了CL-20和TKX-50的表面静电势能,结果如图7所示。
图7 CL-20和TKX-50表面静电势能分布图
Fig.7 Surface electrostatic potential energy distribution map of CL-20 and TKX-50
表3列出了CL-20和TKX-50所对应的静电势能正负极值点,这些点最易于产生静电吸引,形成分子间非共价键。
表3 静电势能正负极值点及对应的基团
Table 3 Ppositive and negative extremum points of electrostatic potential energy and corresponding groups
由图7和表3可知,CL-20中带有硝基的基团在—NO2的O部分所带有的电子最为密集,这也表示这片蓝色区域容易与TKX-50分子中红色的电子贫乏区域(—NH+3)相互吸引、互补,进而形成稳定的非共价键力。依据XRD、IR、Raman、MS分析可知,CL-20/TKX-50共晶的成功制备,并且CL-20中—NO2和TKX-50中—NH+3之间形成氢键是共晶形成的主要驱动力。
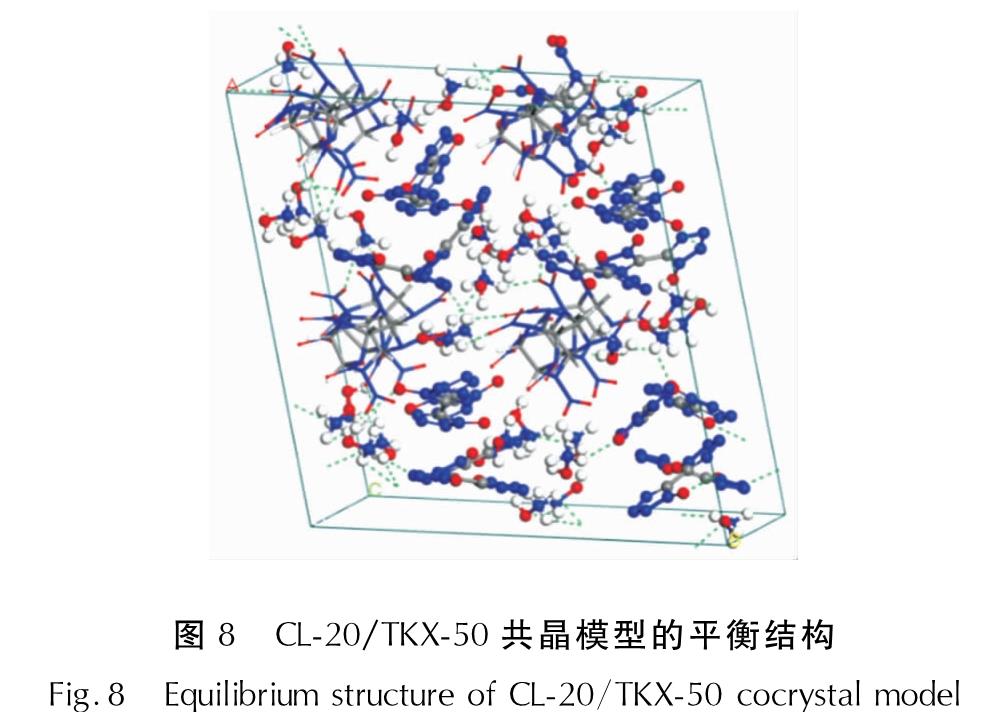
建模分析:首先,对单个分子进行优化; 然后利用Materials Studio 5.0软件的Amorphpus Cell模块通过优化好的分子构建摩尔比为1:2的模型。利用Forcite模块进行几何优化,优化细节与静电势能分析一致。最后,对优化好的模型进行分子动力学模拟; 模拟细节采用Compass力场,设置步长为1fs,温度控制方法为Velocity scale,静电作用和范德华力相互作用分别设为Ewald和atom-Xbased方法,总模拟时长为100ps,获得模拟平衡结构,并对模拟结果进行分析。图8为体系的平衡结构。
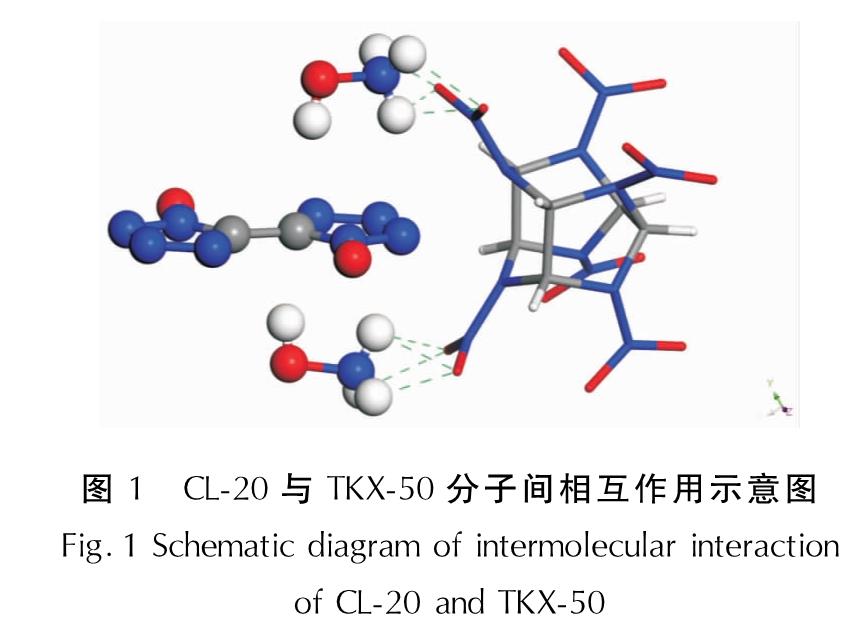
图8 CL-20/TKX-50共晶模型的平衡结构
Fig.8 Equilibrium structure of CL-20/TKX-50 cocrystal model
图8中虚线代表氢键,通过构建CL-20/TKX-50共晶模型,并进行分子动力学分析可知,CL-20分子和TKX-50分子间可以较好地产生氢键相互作用。如图8所示,CL-20中—NO2的O与TKX-50中—NH+3的H之间形成了氢键,这与表面静电势能分析结果具有较好的一致性。