作者简介:刘石硕(1997-),男,硕士研究生。E-mail: liushishuo0709@163.com
通信作者:刘杰(1987-),男,副教授,博导。E-mail:jie_liu_njust@126.com
(1.南京理工大学 化学与化工学院&国家超细粉体工程技术研究中心,江苏 南京 210094; 2.湖北航天化学技术研究所,湖北 襄阳 441003)
(1.School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Nanjing University of Science and Technology & National Special Superfine Powder Engineering Research Center of China,Nanjing 210094,China; 2.Hubei Institute of Aerospace Chemical Technology,Xiangyang Hubei 441003,China)
physical chemistry; ammonium dinitramide; ADN; spherical; hygroscopic; composite particles; impact sensitivity
DOI: 10.14077/j.issn.1007-7812.202207008
复合固体推进剂主要由强氧化剂、燃烧剂、黏结剂、固化剂等组分组成,是实现武器远程打击、完成卫星发射和宇宙探索的重要动力源,在国防现代化建设与国民经济发展中发挥着非常重要的作用[1-6]。二硝酰胺铵(NH4N(NO2)2,简称ADN)是一种高能强氧化剂,不含卤素,其热分解燃烧产物比较洁净(如氮气和水),无HCl等引起的推进剂特征信号增强及酸雾或酸雨污染等问题。并且,ADN还具有能量高的优势,若能取代高氯酸铵(AP)之类的常规氧化剂应用于复合固体推进剂中,还可使推进剂的能量显著提高[7-12]。这使得ADN在高能、绿色、低特征信号推进剂中具有广泛的应用前景[13-14]。然而,ADN极易吸湿、易团聚结块,导致推进剂工艺性能恶化进而难以有效加工成型,这是制约其大规模实际应用的关键技术难题[15-16]。此外,ADN与复合固体推进剂配方体系中的异氰酸酯固化剂的相容性也较差,会影响推进剂的固化,进而影响推进剂成型并导致其力学性能降低; 另外,ADN的感度较高,使得推进剂在加工制造、运输及使用过程中的安全风险增大[17-20]。
对ADN进行物理化学改性,主要包括球形化、表面包覆、共晶等方法。球形化处理,是降低ADN吸湿性的有效途径。俄罗斯、美国、德国、瑞典等国曾采用雾化结晶或乳液结晶球形化技术,制备得到了球形ADN,降低了ADN的吸湿性,俄罗斯等国虽未给出具体吸湿性数据,但已将其实际应用于推进剂体系中[17, 21]。我国也于近年来实现了ADN的球形化制备,但是仍然因其在实用环境中吸湿性较强而未获得大规模实际应用[22-25]。因此,结合上述问题,应选择适当的表面处理措施,研究出更加有效的改性技术途径,使ADN能够真正大规模应用于我国复合固体推进剂中。表面包覆是改善ADN吸湿性的另一种行之有效的途径。国内外研究工作者大量采用高分子黏结剂(如端羟基聚丁二烯、乙基纤维素等)、偶联剂(如KH-550)、表面活性剂(如十八烷胺),以及石蜡、硬脂酸、石墨烯等对ADN进行包覆处理,如卢先明等[15, 26-29]以GAP/丁二酸二丙炔醇酯(BPS)交联体为包覆材料,使ADN吸湿率降低了10%,进而在一定程度上降低了ADN的吸湿性。再如采用石蜡对ADN包覆(浸润)处理后,再进一步采用高分子黏结剂进行二次包覆处理,能获得比较理想的防吸湿效果。然而这些包覆剂往往都不是推进剂中既有的物质,其引入会引起推进剂体系相容性变差,影响推进剂的力学性能、安全性能等。并且这些包覆剂通常都是“惰性”物质,一方面会导致推进剂的能量降低; 另一方面会阻碍ADN的热分解及与推进剂其他组分的燃烧化学反应,使得推进剂的燃烧性能受到大幅度影响且表现为不可控,进而影响推进剂的能量释放,使推进剂的性能达不到设计指标要求而无法使用。
本研究采用吸湿性较弱、感度较低、与复合固体推进剂组分相容性良好且已经获得成熟应用的强氧化剂AP,对具有强吸湿性的强氧化剂ADN进行表面包覆改性处理,通过构建强吸湿-弱吸湿核(ADN)壳(AP)复合双元强氧化剂这种新型复合材料的思路,利用 AP壳层的阻隔与缓冲作用及其与推进剂体系具有良好相容性的特性,进而改善ADN的吸湿性与推进剂的兼容性,为促进ADN大规模实际应用、减少推进剂中AP用量提供理论指导和技术支持。
二硝酰胺铵(ADN),洛阳黎明化工研究设计院有限责任公司; 高氯酸铵(AP),大连北方氯酸钾厂; 环己烷(C6H12)、九水合硝酸铁(Fe(NO3)3·9H2O),均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司; 异丙醇(IPA)、十二烷基苯环酸钠(SDBS),均为分析纯,阿拉丁试剂有限公司。
S-4800 II型场发射扫描电子显微镜,日本Hita-chi公司; Tencai G2 F20 S-TWIN型透射电子显微镜,美国FEI公司; Advanced D8型X射线衍射仪,德国Bruker公司; Nicolet iS 10型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司; SDT Q600型TG/DSC同步热分析仪,美国TA公司; HGZ-3型撞击感度仪,南京德控科技有限公司; HWHS-150恒温恒湿箱,盐城欧莱克科技有限公司。
配置0.1g/mL ADN的异丙醇饱和溶液,加入硝酸铁与十二烷基苯环酸钠溶解于ADN的异丙醇饱和溶液中。在恒温槽控制的特定条件下,将上述ADN溶液缓慢滴加到ADN的非溶剂环己烷当中,使ADN重结晶形成球形ADN。
将原料ADN与原料AP按照质量比4:1称取,放置于玛瑙研钵内研磨使之混合均匀,得到ADN/AP混合样。
配置0.0167g/mL AP的乙醇饱和溶液,将球形ADN分散在非溶剂环己烷当中,ADN与AP的质量比为4:1。在恒温槽控制的特定条件下,将AP溶液缓慢滴加至含球形ADN非溶剂环己烷当中,使AP重结晶包覆在球形ADN上,形成ADN@AP复合粒子。
采用场发射扫描电子显微镜观察样品的表面形貌和内部结构; 采用X射线衍射仪测定样品的晶型,选择Cu-Ka靶,操作电压40kV,操作电流40mA,步长为0.05°,扫描范围(2θ)为10°~80°; 采用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪测定样品的分子结构,测试条件:扫描范围为4000~500cm-1,光谱分辨率为0.4cm-1; 采用TG/DSC同步热分析仪测试样品的热分解性能,测试条件为:Al2O3坩埚,Ar气氛,气体流速为50mL/min; 采用DSC/TG-FTIR联用测试样品分解产生的气体,测试条件为:Al2O3坩埚,Ar气氛,气体流速为50mL/min。
根据 GJB 770B-2005《火药试验方法》601.2中的方法对样品进行撞击感度测试。测试条件为:落锤质量5kg,药量(50±1)mg,测试温度(293.15±2)K,相对湿度(60±5)%,以特性落高(H50)表征撞击感度; 参照国军标“GJB77A-1997火炸药平衡器法”测试了其绝对吸湿率,将待测材料在50℃的真空干燥箱中干燥至恒重后,称取5~10g样品,精度为0.001g,测试条件为环境温度30℃,湿度75%。
原料ADN、球形ADN、直接研磨得到的ADN/AP混合物和ADN@AP复合粒子的SEM照片如图1所示。
图1 原料ADN、球形ADN、ADN/AP混合物和ADN@AP复合粒子的SEM照片
Fig.1 SEM images of raw ADN, spherical ADN, ADN/AP mixtures and ADN@AP composite particles
由图1可以看出,原料ADN成棱柱状,棱角分明,表面粗糙,粒径在200~300μm; 而溶剂-非溶剂法制备得到的ADN成球形,分散性好,平均粒径在50μm左右; 直接研磨得到的ADN/AP混合物形貌不规则,并且通过EDS面扫图,可以直观地看出样品上的元素分布,元素Cl的分布杂乱,说明AP只是零散附着在ADN表面。而溶剂-非溶剂法制备得到的ADN@AP复合粒子,EDS面扫图上元素Cl均匀分布,说明AP均匀地包覆在ADN表面,并且整体形貌成类球形。
原料ADN、球形ADN、原料AP、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子的XRD谱图如图2所示。
图2 原料ADN、球形ADN、原料AP、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子的XRD谱图
Fig.2 XRD spectra of raw ADN, spherical ADN, raw AP, ADN/AP mixture and spherical ADN@AP composite particles
由图2可知,ADN/AP混合样特征衍射峰的位置与原料相比并无特别明显的变化,但是混合样位于19.12°、24.52°的特征峰与原料AP的相比不明显,这是由于混合样中AP的含量较少,所以与ADN相比峰强较弱,而球形ADN和ADN@AP复合粒子特征衍射峰的位置和强度与原料相比发生了变化,ADN原料衍射峰分别位于13.03°、14.87°、17.67°、26.23°、27.02°、27.62°、30.29°、39.80°和44.34°,分别对应于ADN的结晶晶面(1 0 0)、(1 1 0)、(0 1 1)、(2 0 0)、(1 2 1)、(0 3 1)、(2 2 0)、(3 0 0)和(1 1 -1)。主要结晶晶面为(1 0 0)、(1 1 0)、(1 2 1)、(2 2 0)和(3 0 0)。而球形ADN衍射峰分别位于13.03°、14.87°、17.67°、26.23°、27.02°、27.62°、29.25、30.29°和39.80°,分别对应于ADN的结晶晶面(1 0 0)、(1 1 0)、(0 1 1)、(2 0 0)、(1 2 1)、(0 3 1)、(0 4 0)、(2 2 0)和(3 0 0)。主要结晶晶面为(1 1 0)、(0 1 1)、(1 2 1)、(0 4 0)、(2 2 0)和(3 0 0)。测试结果表明,球形ADN在重结晶过程中不仅形貌发生了改变,同时(1 2 1)和(0 4 0)晶面生长变快,成为主要结晶晶面。而ADN@AP复合粒子与ADN/AP混合样相比,没有晶面的变化,说明ADN@AP复合粒子只是AP均匀地包覆在ADN的表面。
原料ADN、球形ADN、原料AP、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子的红外光谱图如图3所示。
图3 原料ADN、球形ADN、原料AP、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子的红外光谱图
Fig.3 FTIR spectrogram of raw ADN, spherical ADN, raw AP, ADN/AP mixture and ADN@AP composite particles
由图3可以看出,原料ADN在3300、1520、1420、1340、1160、1000、830、760、720cm-1附近出现吸收峰,位于3300cm-1处为N—H的伸缩振动峰,位于1520cm-1和1420cm-1附近为—NO2伸缩振动峰,位于1340、1160cm-1附近为—NO2对称伸缩运动峰、位于1000cm-1附近为—N3对称伸缩运动峰、830、760、720cm-1附近为—NO2弯曲振动峰。AP分别在3300、1420、1030、930、625cm-1附近出现吸收峰,经分析位于3300cm-1处为N—H的伸缩振动峰,位于1420cm-1附近为N—H的弯曲振动峰,位于1030、930、625cm-1附近为ClO-4的伸缩振动峰。通过对比原料可知,球形ADN、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子的特征吸收峰的位置与原料基本一致,说明重结晶过程中ADN与AP的分子结构没有发射改变。由于ADN/AP混合样的AP含量较少,AP的ClO-4的伸缩振动特征峰吸收强度较弱,而ADN@AP复合粒子由于AP均匀包覆在ADN的表面,使透过的红外光能量有所衰减,不能使核壳结构的ADN核的分子产生振动和转动,从而不能产生红外吸收,导致1000cm-1附近的吸收峰被相邻的AP较强的ClO-4的伸缩振动峰所掩盖,这说明了AP较好地包覆在了ADN的表面。
原料ADN、球形ADN、原料AP、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子在升温速率为10℃/min时的DSC-TG曲线如图4所示; 在升温速率分别为5、10、15、20℃/min时的DSC曲线如图5所示。
图4 原料ADN、AP、球形ADN、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子的DSC-TG曲线
Fig.4 DSC-TG curves of raw ADN, AP, spherical ADN, ADN/AP mixtures and ADN@AP composite particles
图5 原料ADN、球形ADN、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子在不同升温速率时的的DSC曲线
Fig.5 DSC curves of raw ADN, spherical ADN, ADN/AP mixture and ADN@AP composite particles at different heating ratess
从图4可以看出,原料ADN和球形ADN热分解过程大概分为两个阶段:晶体熔融阶段和分解阶段,表现在DSC曲线上有一个吸热峰和一个放热峰,表现在TG曲线上只有一个失重过程。球形ADN、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子与原料ADN相对比ADN的分解峰温变化不大,ADN/AP混合样的AP高温分解峰温比原料AP降低41.51℃,但由于混合样中AP的含量较少,导致放热峰不明显。而ADN@AP复合粒子的AP低温分解峰与高温分解峰合并为一个分解峰,放热更集中,效果更好,说明ADN对AP的热分解起到了促进效果。
采用Kissinger法,根据下面公式计算不同ADN样品的表观活化能(Ea)和指前因子(A)等热分解动力学参数。不同ADN样品的动力学参数如表1所示。
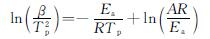
式中:β为升温速率,K/min; Tp为热分解峰峰温,K; Ea为表观活化能,kJ/mol; R为气体常数,8.314J/(K·mol); A为指前因子,s-1。
表1 原料ADN、球形ADN、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子的动力学参数
Table 1 Dynamic parameters of raw ADN, spherical ADN, ADN/AP mixtures and ADN@AP composite particles
由表1可知,对比原料ADN,球形ADN、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子的ADN分解反应活化能降低,特别是ADN@AP复合粒子相比原料反应活化能降低35.1kJ/mol。说明通过对ADN进行球形化与包覆,对ADN的分解反应有一定的促进效果,使反应更容易进行。并且通过AP包覆ADN形成复合粒子的手段,对ADN分解反应的促进效果更为有效。
现有研究结果表明[30-32],ADN热分解过程主要发生的反应为:
ADN→NH3+HDN (1)
ADN→NH3+N2O+HNO3 (2)
ADN→N2O+AN (3)
HDN→N2O+HNO3 (4)
HDN→NO2+HNNO2 (5)
NH3+HNO3→AN (6)
在ADN的分解过程中,中间产物HDN不稳定,生成后快速分解,而反应中生成的HNO3和NH3能快速发生反应(6),因而反应(3)可以看作是反应(1)、(2)、(4)和(6)作用的结果。而AP热分解过程主要发生的反应为:
NH4ClO4→NH3+HClO4 (7)
2NH3+2HClO4→N2↑+4H2O+Cl2↑+2O2↑ (8)
常温下,AP能稳定存在,240℃左右时由斜方晶型转化为立方晶型,加热至 260℃升华,300℃时逸出褐色蒸气,400℃时发生燃烧。350℃左右部分AP表面分解生成吸附态的NH3和HClO4; 随着温度继续升高,NH3和HClO4解吸,发生氧化还原反应。
对原料ADN、ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子进行DSC/TG-FTIR联用测试,升温速率为10℃/min,其不同时刻气体产物的红外光谱图如图6所示。由图6可知,与原料相比,ADN/AP混合样以及ADN@AP复合粒子的NO2和NO2气体生成提前了,特别是ADN@AP复合粒子的NO2气体生成比原料提前了3.2min。结合ADN和AP的分解反应,可以推断因为ADN的热分解先于AP,分解过程中产生的中间产物NH3被AP吸附,使ADN的反应(1)和(2)更有效地进行,从而使反应(4)和反应(5)也随之提前,导致了NO2和NO2气体生成提前了。最终使ADN的反应活化能下降。而AP吸附ADN产生的NH3使自身低温分解反应被抑制,但同时促进了高温分解反应,导致低温分解峰后移、高温分解峰前移,使AP的放热更集中。
对原料ADN、AP、球形ADN、ADN/AP混合物和球形ADN@AP复合粒子进行撞击感度测试,测试结果如表2所示。
由表2可以看出,与ADN原料相比,ADN/AP混合物和ADN@AP复合粒子的H50分别增加11.05cm和19.02cm,即二者的撞击感度分别降低58.16%和100.10%。简单的机械混合物ADN/AP可以使撞击感度降低,但通过溶剂-非溶剂法制得的ADN@AP复合粒子降感作用更显著,并且ADN@AP复合粒子的撞击感度标准偏差更小,置信度更高,性能更稳定。
表2 原料ADN、AP、球形ADN、ADN/AP混合物和ADN@AP复合粒子的撞击感度
Table 2 Impact sensitivity of raw ADN, AP, spherical ADN, ADN/AP mixtures and ADN@AP composite
根据“热点理论”[33],含能材料的撞击过程是将冲击动能转化为材料热能,在此过程中,含能材料颗粒的孔隙绝热压缩形成局部热点,从而导致材料产生爆燃现象。ADN/AP混合物和ADN原料形貌都不规则,在受到外力撞击时,机械能转变成热能,首先聚集在棱角、孔隙等表面能高的地方形成局部热点,热分解反应首先发生,反应放出的热量又加速热分解,导致热点部位爆炸,最终扩散引发整体爆炸。ADN原料具有棱角,颗粒间的空隙很大,不利于颗粒之间的热传导和热散失,容易形成热点。而球形ADN形状规则,表面平整,使得总接触面积增大,起到提高ADN颗粒间热传导的作用,不易形成局部积热,因此较原料ADN相比,撞击感度降低。AP的感度低于ADN,所以在AP的作用下,ADN/AP混合物和ADN@AP复合粒子相比于原料ADN,撞击感度降低。而ADN@AP复合粒子呈类球形,空隙率低,内部缺陷少,在受到外力撞击时,不易形成局部热点,因此撞击感度大幅度降低。
为定量表征ADN包覆材料的降吸湿性能,对原料ADN、球形ADN、ADN/AP混合物和ADN@AP复合粒子进行吸湿性测试,测试结果如图7所示。
图7 原料ADN、球形ADN、ADN/AP混合物和ADN@AP复合粒子的绝对吸湿率对比图
Fig.7 Comparison of hygroscopicity of raw ADN, spherical ADN, ADN/AP mixture and ADN@AP composite particles
根据ADN的吸湿机理[34],ADN的吸湿主要分为两个阶段:第一阶段为水蒸气固态ADN表面的多分子层吸附,该阶段内ADN吸湿的主要因素为水蒸汽与ADN之间的作用力和ADN与水蒸汽之间的接触面积; 第二阶段为多分子层上的毛细孔凝聚,ADN表面的光滑程度与形貌为该区域ADN吸湿的主要影响力。由于与原料ADN相比,球形ADN、ADN/AP混合物和球形ADN@AP复合粒子的粒径较小,比表面积较大,水蒸汽更易吸附,所以在第一阶段的吸湿性略强于原料,但当吸湿进入第二阶段,由于球形化与AP的保护,在12h之后,原料ADN绝对吸湿率已达到18.5%,变成水溶液,而球形ADN、ADN/AP混合物和球形ADN@AP复合粒子仍然保持较好的状态,具有一定的抗吸湿性,特别是ADN@AP复合粒子相比于原料ADN在24h后绝对吸湿率从23.5%降为8.2%,吸湿性明显降低。
(1)使用溶剂-非溶剂法制备出的球形ADN与ADN@AP复合粒子,分散性较好,形状规则。重结晶制备出的球形ADN和ADN@AP复合粒子与原料相比组分不变,但晶型发生了变化。
(2)ADN@AP复合粒子使AP两个分解峰合并为一个分解峰,放热更集中,分解效果更好,并且ADN的Ea相比原料ADN降低35.1kJ/mol,即反应活化能降低了32.1%。实验表明,由ADN与AP形成的复合粒子对两种组成物的热分解有促进作用。
(3)通过引入AP与ADN复合,能对ADN实现降感,提高ADN的安全性。与ADN原料相比,ADN/AP混合样和ADN@AP复合粒子的H50分别增加11.05cm和19.02cm,即撞击感度分别降低58.16%和100.10%。
(4)球形化ADN与用AP包覆的ADN,能够明显降低ADN的吸湿性,特别是ADN@AP复合粒子相比于原料ADN,在24h后绝对吸湿率从23.5%降至8.2%,吸湿性明显降低。